Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 1
Android Cell Phone Basics
Table of Contents
Google Accounts ............................................... 2
The Device ........................................................ 2
Status Bar ......................................................... 2
Notifications ..................................................... 3
Gestures ............................................................ 3
Quick Settings ................................................... 3
Settings ............................................................. 4
Accessibility ...................................................... 5
Font Size ........................................................... 5
Flash Alerts ....................................................... 6
Android Version vs Phone Model vs Carrier.... 6
Lock Screens and Security ................................. 7
Turning On Your Lock Screen .......................... 7
Home Screens .................................................... 7
Apps or Folders on the Home Screen .............. 8
Widgets ............................................................. 9
Common Icons................................................ 10
Common Apps ................................................ 10
Contacts ........................................................... 12
Viewing Contacts on Your Phone .................... 12
Syncing Contacts ............................................. 13
Editing Gmail Contacts on the Web ................ 13
Emergency Calls and Contacts ........................ 14
To Make an Emergency Call ............................ 14
Emergency Contacts ........................................ 16
Wireless .......................................................... 18
Secured vs Unsecured Wireless Networks ..... 18
Texting ............................................................ 18
Text Messages and Phone Data ...................... 18
Text Messages ................................................. 19
Alternatives to SMS Texting ........................... 20
Apps ................................................................ 20
Closing and Removing Apps .......................... 20
Google Play Store ............................................ 21
Folders ............................................................ 23
Camera ............................................................ 25
Photos ............................................................. 26
Sharing ............................................................ 27
SD Cards ......................................................... 27
Saving New Pictures to the SD Card .............. 29
Google Drive ................................................... 29
Setting Up Google Drive on Your PC ..............31
Backup and Sync ............................................. 33
Bluetooth ........................................................ 34
Smart Lock ...................................................... 35
Email ............................................................... 35
Music ............................................................... 35
Podcasts .......................................................... 35
Texting Acronyms ........................................... 37
Emoticons ....................................................... 38
Technology Glossary ................................... 39
Index ............................................................... 48
There is a glossary at the end of this hand out that defines and explains acronyms and technical terms,
and an index to quickly find how to do a particular task!
Updated: 23 June 2021
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 2
Google Accounts
Android is Google’s operating system, and as such things will be easier for you if you sign in with a
google account. If you already have gmail, then you already have a google account.
Before you get ready to set up your phone, find your gmail address and password. If you are not sure
what your password us, you can reset it from the gmail website. (https://myaccount.google.com)
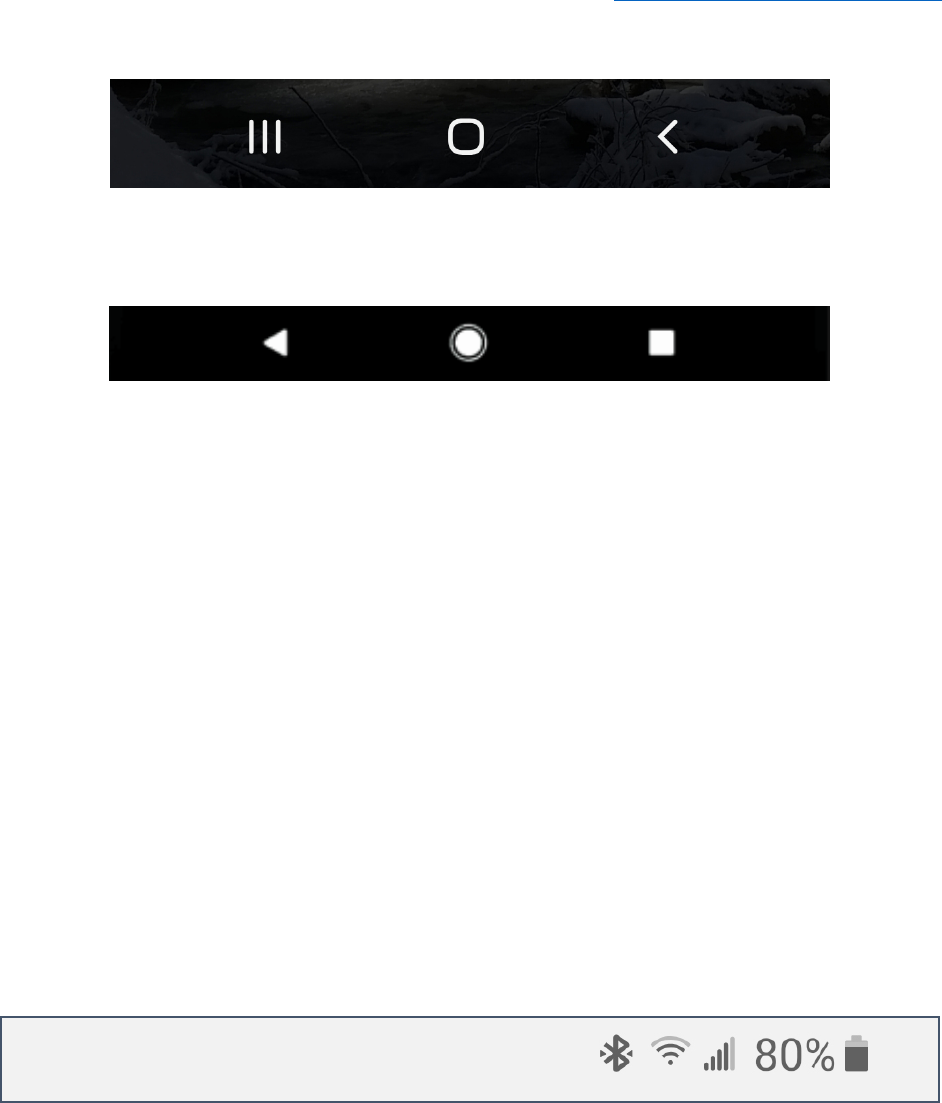
The Device
Overview Home Back
Back Home Overview
Android devices will generally have three buttons (either physical or digital) along the bottom. On
older devices, the center or home button may be a physical button. On newer devices, all three
buttons may be digital.
The “Overview Button” lets you scroll through all currently open apps. This is also where you go if you
want to close all currently running apps.
The middle button is the “Home Button”. On older devices this may be a physical button on your
device. Tapping the Home button will always take you back to what you have designated as your main
screen. You can organize your device screens so that your most important apps and widgets are
available on your primary Home Screen.
The “Back Button” is generally a triangle or less than sign. If you aren’t sure of what is going on,
retreat from your current position using the Back button. You can usually tap the back button
multiple times to return to a previous menu option or setting.
If you don’t see those three buttons, swipe up from the bottom of the screen to make them appear.
Status Bar
The status bar appears at the top of the phone screen. On the right side of the status bar you typically
have icons letting you know the status of your data, wireless, and Bluetooth, as well as how full or
empty your battery is.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 3
Notifications
On the left side of the status bar are your notifications—if you have an unread email or text message,
or a missed phone call, you can tell from looking at this section of the status bar.
Gestures
There are many different gestures you can use to manipulate your device.
Swipe down from the top of the screen with one
finger
Quick settings
Pinching two fingers together
Minimize text / images
View home screen options
Swipe up from the middle of the screen with one
finger
Open App drawer
Swipe down from top of app window
Refresh
Long press an icon
Move / remove an icon
Keep in mind that getting a stylus (capacitive pen) can be very helpful in manipulating your device if
you feel like you’re often hitting the wrong icons or letters.
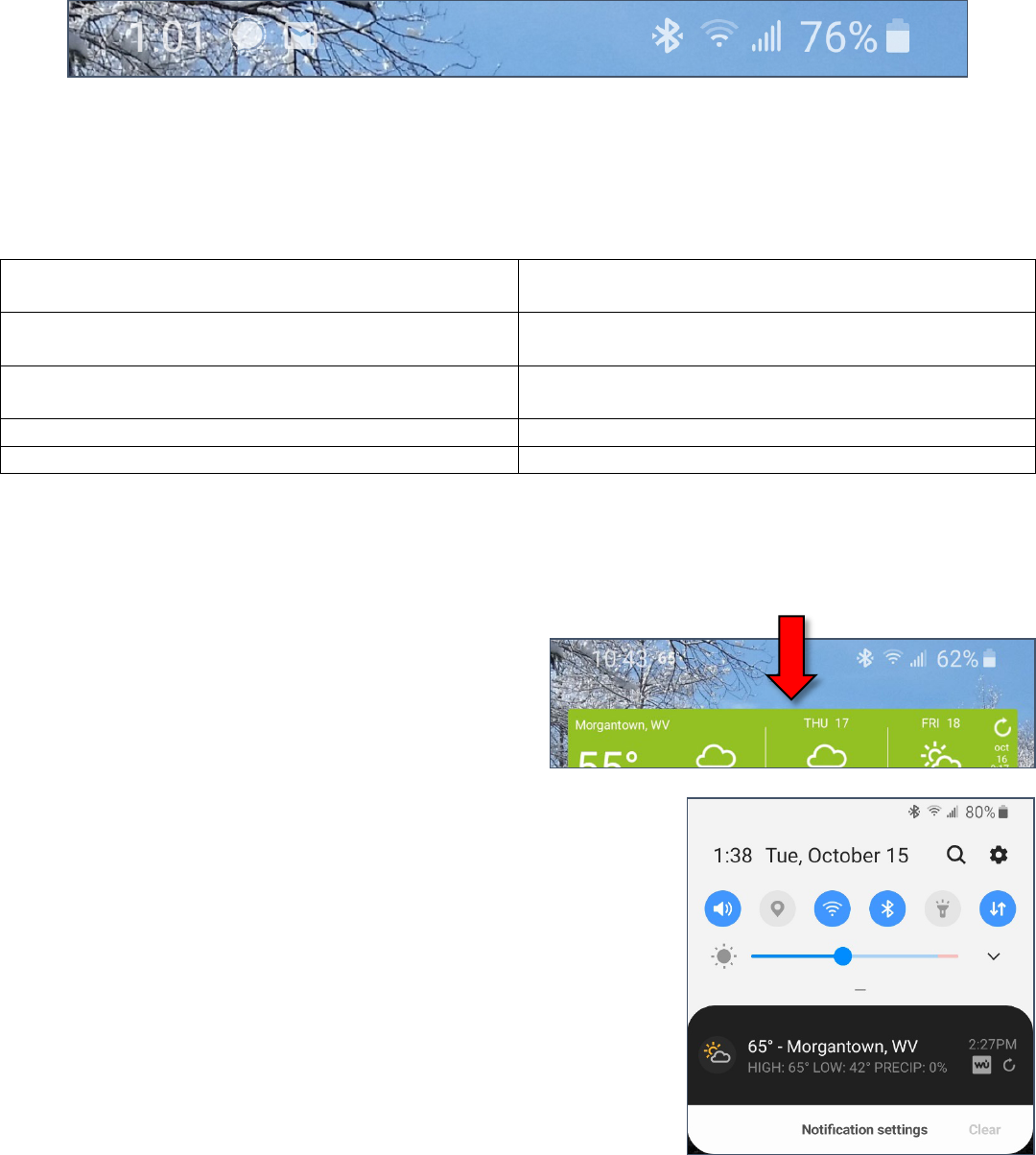
Quick Settings
Quick settings is the area of the phone I go to most
frequently. You access it by pulling down from the
Status bar at the top of the screen.
By default, there are toggles there for things like volume and
Bluetooth, but you can modify this are to make the toggles you
use most available at the top. (For those with limited cell plans,
you can put a toggle for mobile data at the top of the list, and I
always move the flashlight toggle to the top.)
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 4
This area is also where you can dismiss the notifications that pile up
in the top left corner of your screen. Once you pull down, you can
select a notification to view more, or you can clear all the
notifications.
Dragging down the small bar below the brightness slider will display
more quick toggles, and is also where you go to edit the order in
which your buttons (quick toggles) are displayed.
Settings
Most of the things you might want to change or personalize will be accessed from
Settings. You can access your settings from quick settings, from an icon on your home
screen (if you have one there—many people don’t) or from your App Drawer. Once you
have your settings open, you can either scroll through the various menus or search from
the Search / Finder box.
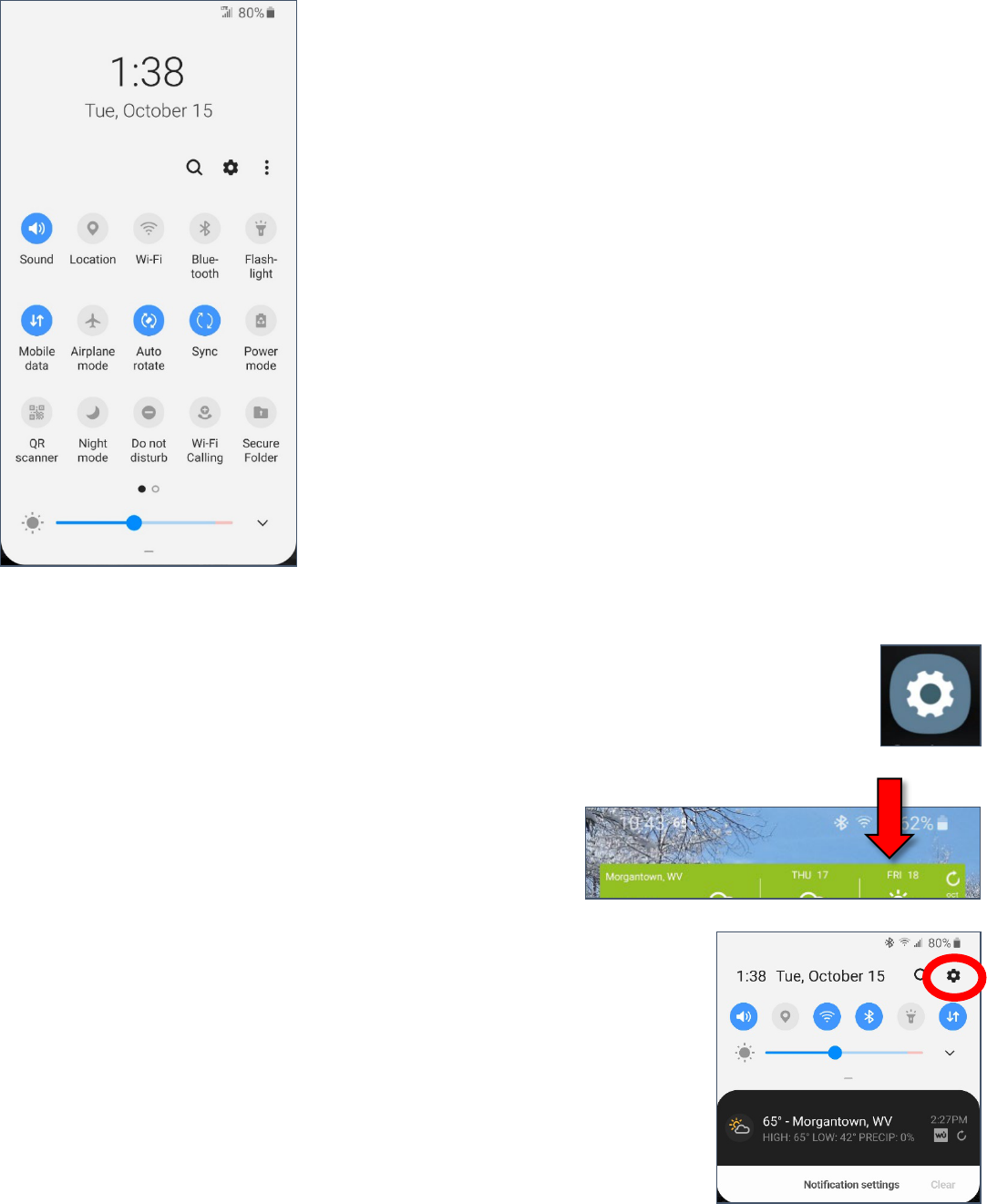
To Access Android Settings
1. Drag your finger down from the top of the screen. It
helps to start a little bit above the active screen.
2. Your Quick Settings will appear. This has toggles for commonly
used services, such as wireless, Bluetooth, and Volume. It should
also have a gear icon which will allow you to open your settings. Tap
on the gear icon to open your device settings.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 5
3. This is where it can get complicated, because different versions of the
Android OS and different phone models will be organized differently.
The easiest way to find a specific setting is to search for it. Look for a
magnifying glass icon, and then tap it.
4. In the Search box, start to type in the setting you want to modify.
5. A list of matches appears, and filters as you type. Once the setting
you need appears, tap it.
Accessibility
There are many different things you can do to make your device easier to use. Many of these options
are located in your Settings under Accessibility, but in this handout we’ll just look at a couple of
individual settings.
Font Size
One of the easiest things to change on your device is to change the
font size. This makes all the text larger.
Changing Font Size
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Search for font.
3. Select Font size and style.
4. Use the slider to make the text larger as needed.
Other useful options under Visibility Enhancements are:
• Larger mouse / touchpad pointer
• Screen zoom
• High contrast theme
• High contrast fonts
1
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 6
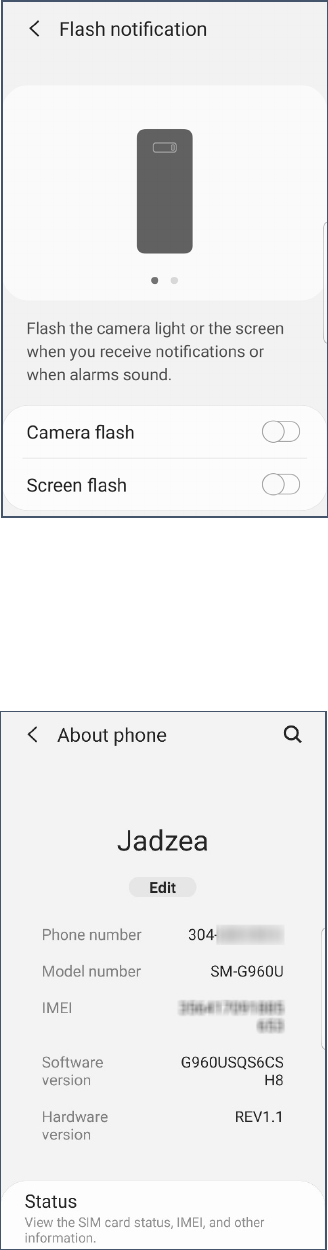
Flash Alerts
Flash alerts cause your camera or screen to flash when you receive a
notification.
Toggling Flash Alerts
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Search for flash.
3. Select Flash notification.
4. Select Camera flash or Screen flash as desired.
Android Version vs Phone Model vs Carrier
Unlike Apple, who mandates that all version of iOS across carriers must look exactly the same, the
versions of Android vary by phone model and by cellular provider. You also have the ability to
customize you operating system. This makes Android devices marvelous to use, but difficult to
support, since no two devices are going to be quite the same.
The information about your device can generally be found in your
device settings, under About phone. Your device model may also
be on the back of your device, but that area is often hidden by a
screen protector.
Finding Your Device Information
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Search for About phone.
Name – You can give you device any name you want. This is often
helpful when connecting via Bluetooth or wireless, since you can
easily recognize your device. Tap Edit to rename your phone.
Model number – This will be something you might need to look up
since the model number displayed isn’t particularly helpful. (The
model number SM-G96OU is a Samsung Galaxy S9 64GB)
Everything else here is probably going to be gibberish to you, but if
someone asks, this is where you’d find it.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 7
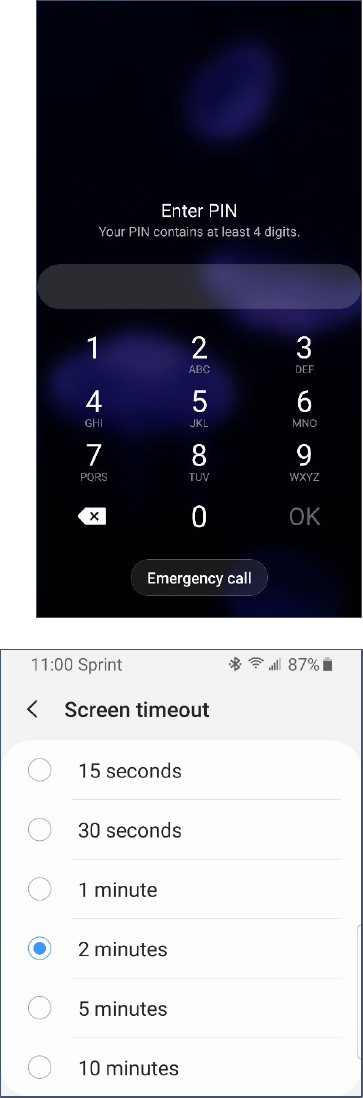
Lock Screens and Security
Your screen should automatically lock when you walk away from
your phone. You have the option of a setting a Pattern, a PIN, or a
Password. I recommend using a PIN (Personal Identification
Number) because it’s more secure than a pattern, but easier to type
than a password. (The keyboard for a PIN is larger.) You can also set
up biometrics, and use your fingerprint or face or iris to login.
If you choose a PIN (recommend) you must have a minimum of 4
numbers. The more digits in your PIN, the more secure your device.
Your lock screen appears after you wake up your phone. From your
lock screen, you have the ability to make an emergency call. (See
page 14)
One thing that makes using a lock screen less painful is to change the
time before your phone locks.
Changing Your Screen Timeout
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Search for Screen timeout.
3. Select Screen timeout.
4. Lengthen the time before your screen timeout occurs.
Turning On Your Lock Screen
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Tap Lock screen.
3. Tap Screen lock type.
4. Select the type of screen lock (I recommend PIN).
5. Set your PIN. I recommend using at least 6 digits.
6. Immediately make note of your PIN in a safe place.
Home Screens
You can have multiple home screens available on your device, or just a single—this flexibility allows
you to customize your device to your preferences. On your screens you can have apps, folders, and or
widgets (small apps that display content such as the weather or your calendar).
You move from screen to screen by swiping left or right on the home screen.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 8
If you are a minimalist, you may want to remove all the individual
apps from your device, leaving just the few you access regularly.
Once you do that, you may have extra home screens—you can
easily remove these.
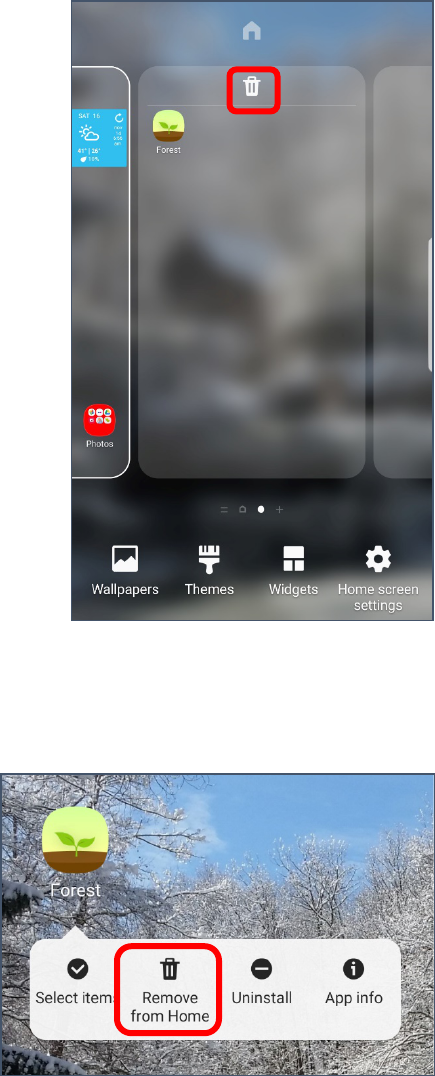
Removing a Home Screen
1. Pinch the screen with two or more fingers.
2. The screen changes to display options for modifying the home
screen.
3. Use your finger to scroll to the extra screen you want to
remove.
4. Tap the trash can icon at the top of the screen.
Conversely, you may want to add an additional home screen,
either to organize your app icons or to add a full screen widget
(like a monthly calendar).
Adding a Home Screen
1. Pinch the screen with two or more fingers.
2. The screen changes to display options for modifying the home
screen.
3. Use your finger to scroll to the far right screen.
4. Tap the plus sign (+) to add an additional home screen.
Apps or Folders on the Home Screen
When you install a new app it typically adds an icon to your home screen. This makes the app easier to
find, but if you prefer a minimalist home screen, it can often clutter things up.
Removing Apps and Folders from the Home Screen
1. Tap and hold the icon you want to remove, until a
menu appears.
2. Tap Remove from Home to keep the program
installed but remove it from your home screen.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 9
Widgets
Widgets are quick links to apps you have installed that often display
information on your home screen. One of the most common widgets
is a weather widget—when open your device, it will display the
current temperature and conditions. Other widgets can display the
number of steps you’ve taken, audio controls, or upcoming
appointments.
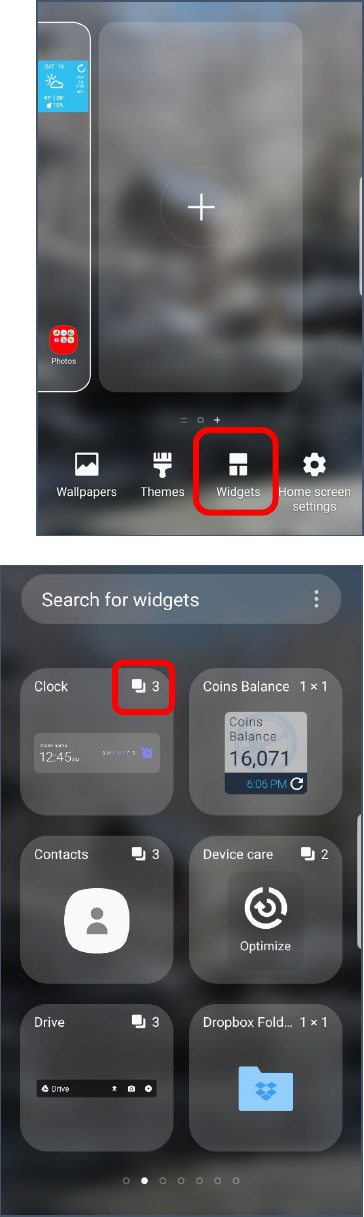
Adding a Widget
1. Scroll to the home screen where you want to place the widget.
2. Pinch the screen with two or more fingers.
3. The screen changes to display options for modifying the home
screen.
4. Tap the Widgets icon towards the bottom of the screen.
5. Swipe with your finger to scroll through the list of available
widgets until you find the one you want. Depending upon the
app, there may be more than one widget available. You can
determine that by looking in the upper right corner of a
widget box. If there is a 2 or 3 (etc) there are different widgets
for that program from which you can choose.
6. Tap to select the widget you want to use. If there are multiple
options, you will be prompted to select the one you want.
7. You can now place the widget precisely where you want on the
screen.
8. Depending upon the program, the app may open to allow you
to customize the widget.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 10
Common Icons
Phone
Call
Delete
Share
Text
Mobile
Data
Volume
Mute
All Off
Email
Airplane
Mode
Bluetooth
Location
/ GPS
Wireless
More
Search
Settings
Common Apps
Phone
Contacts
Email
Camera
Messages
Files
Play Store
Gallery
Phone – Bring up the dial pad to make phone calls.
Contacts – Brings up the directory of everyone in your address book.
Email – The default email application on your device.
Camera – The camera for your device.
Messages – The default text messaging app for your phone.
Files – The app that lets you browse through the various files on your device.
Play Store – The Android app store where you go to find different programs for your device
Gallery – The default location to scroll through the pictures on your device.
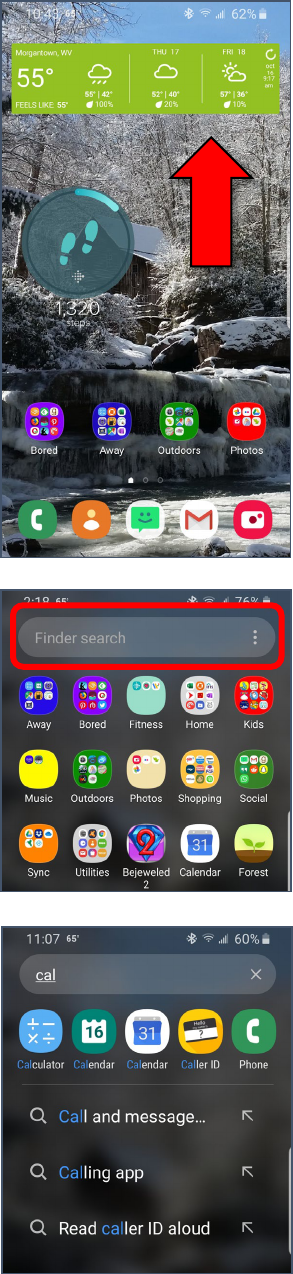
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 11
Opening your App Drawer
1. Place your finger in an empty area of your screen and swipe UP.
2. Most of your apps should be available from here. You can have many
many screens worth of apps, or, you can create folders and place
individual apps in them. So just as with settings, the easiest way to
find an app is to search for it. At the top of the screen, tap in the
Finder / Search box. Begin to type in the name of the app for which
you are searching.
3. As you type, a list of matching apps and settings appears. Tap one of
the icons to open that specific app. Tap the text underneath the icons
to open a setting or informational dialog to make sure everything
meets your privacy preferences.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 12
Contacts
Although you have the option to have your contact list exist only on your phone, it is
recommended to have your contacts synced to the cloud. This means that not only does
your address book follow you from device to device, but also allows you to edit your
address book on a computer, rather than having to make changes on your phone.
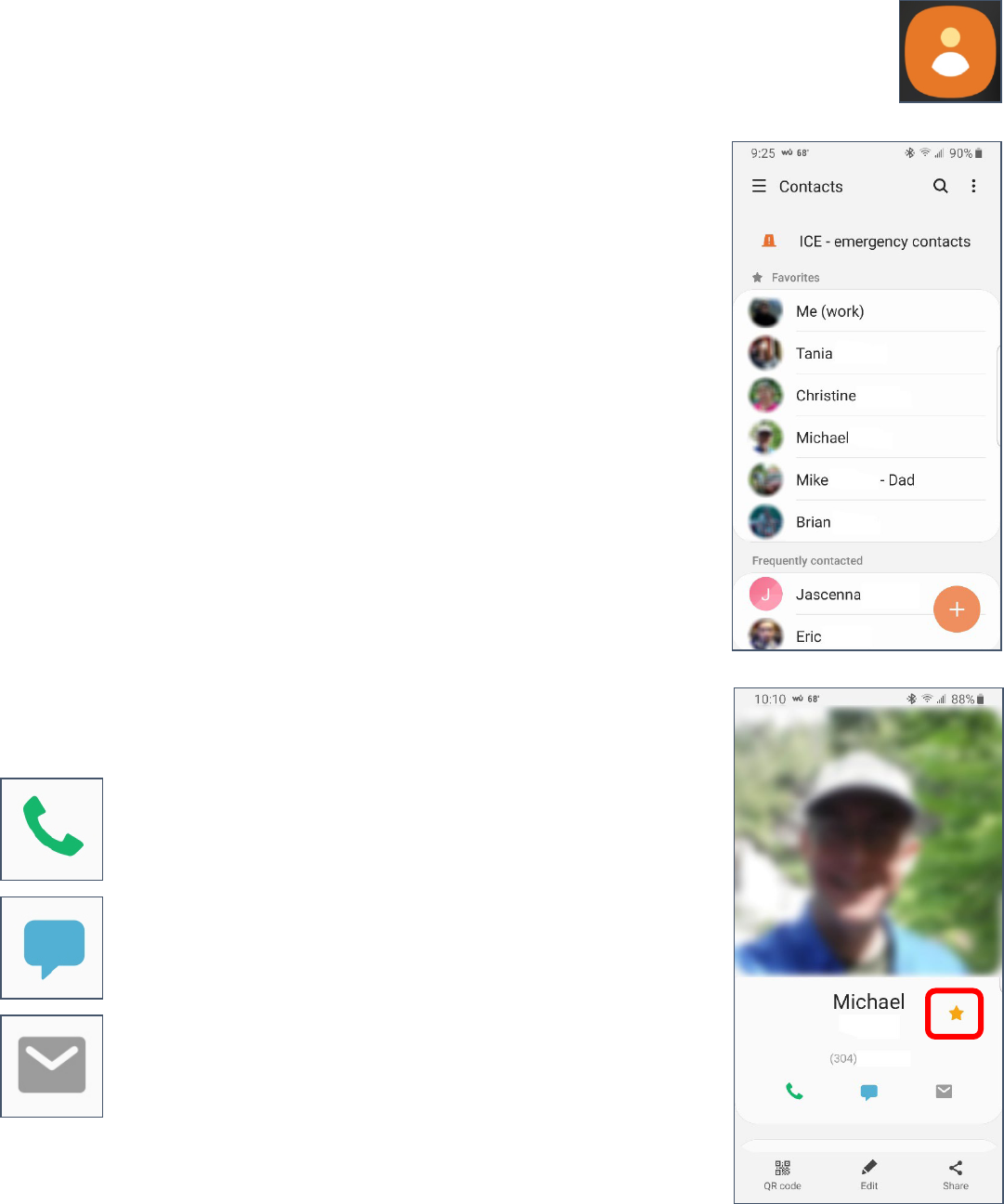
Viewing Contacts on Your Phone
1. Tap the Contacts icon.
2. Your address book opens. You can scroll through the list and select a
contact.
3. You can add a new contact by tapping the plus sign (+) icon in the
lower right corner.
4. The screen changes to display the selected contact. There are three
options directly below the contacts name.
5. Tap the star to make contact a Favorite.
6. Tap the Edit (pencil) icon to modify the information for the selected
contact.
7. Scroll down to the address. Tap on the GPS icon beside the address
to open that location in Google Maps.
Call
Text
Email
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 13
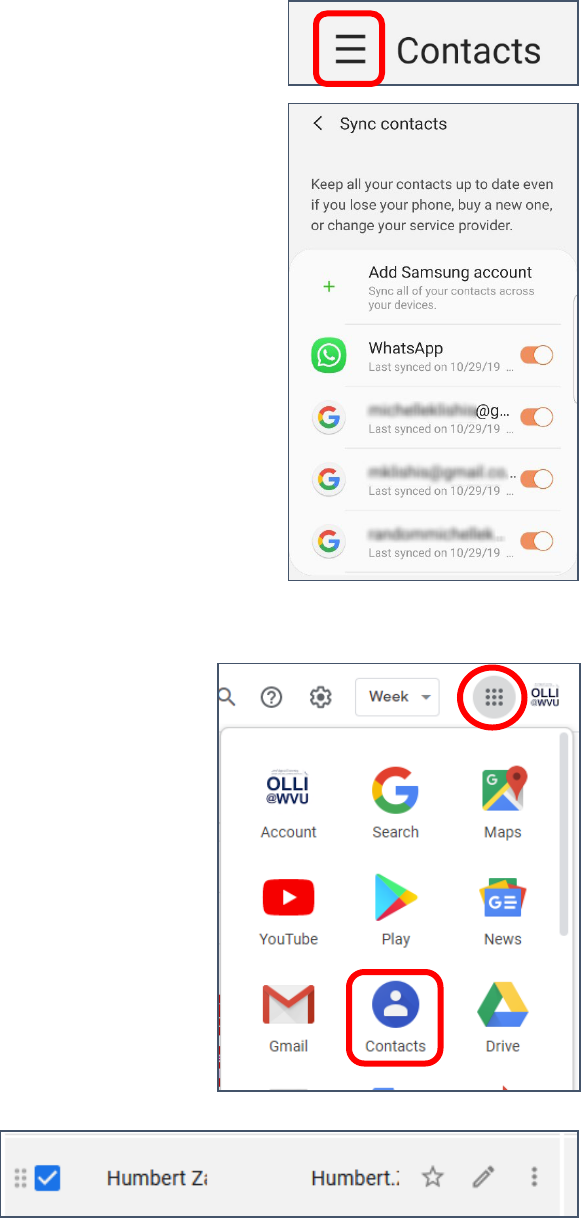
Syncing Contacts
You have the option to sync (or not) the address book attached to any email account on your device.
Selecting what Accounts are Synced
1. Open your Contacts (this is not the same was open the dialer and
selecting contacts from there).
2. On the left side of your contacts screen, click the three parallel lines
or three dots to view more options.
3. Scroll down until you see Manage Contacts and tap.
4. Tap on Sync contacts.
5. A list of your email and messaging accounts is displayed. Toggle the
accounts to select what is synced.
Editing Gmail Contacts on the Web
You can edit your address book from the web as well as from your
phone, including setting favorites and ICE contacts.
1. Log into your Gmail account.
2. Tap on the Google apps icon (the square of squares).
3. A menu of icons appears. If you do not see contacts tap More.
4. Tap the Contacts icon.
5. Your address book opens.
6. When you hold your cursor over a single
address, you will see on the far right of
the screen an Edit option.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 14
7. When you hold your cursor over the icon / picture beside
someone’s name, a check box appears. You can select
multiple contacts using the text box.
8. The icons that appear along the top of the screen when you
select multiple contacts allow you to do things like merge
duplicate contacts into a single contact, or send an email
message to all the selected contacts.
Emergency Calls and Contacts
Emergency calls can be made without having to unlock your phone. Generally they are made to
existing contacts that have been designated as ICE or Emergency contacts.
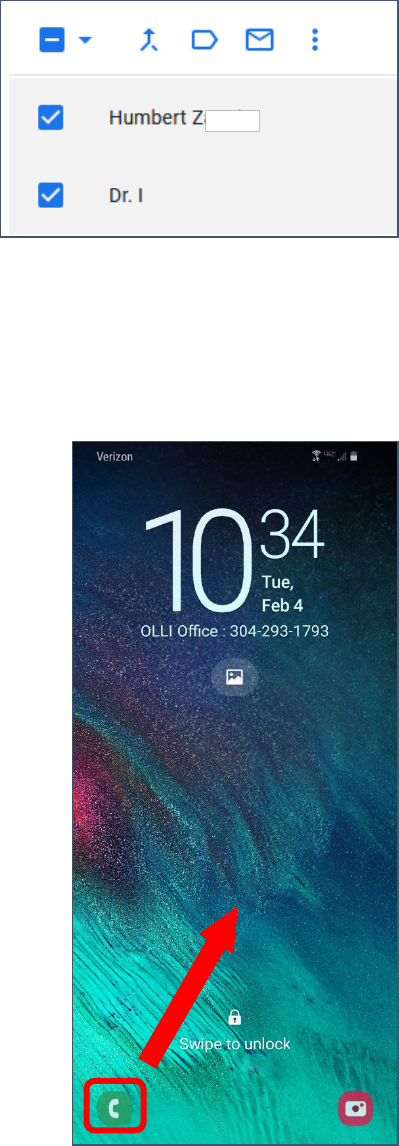
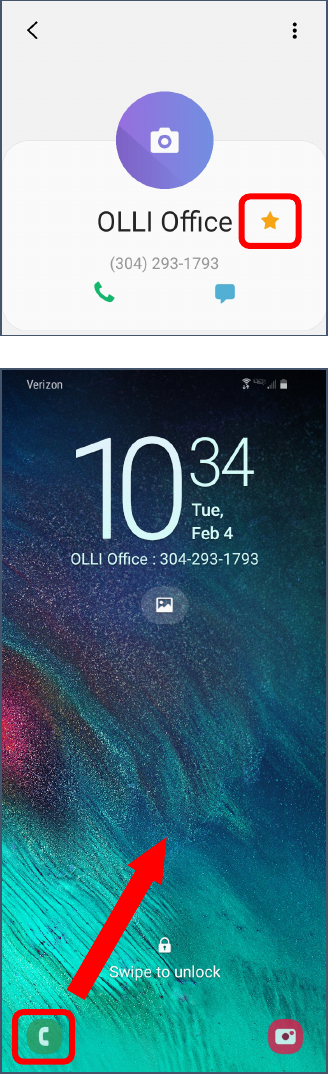
To Make an Emergency Call
1. Wake up the phone.
2. In the lower left corner, swipe up from the phone icon.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 15
3. Tap the Emergency or Emergency
Call button.
4. The emergency call screen appears. You can call an emergency
contact (if listed) or dial emergency services with the keypad.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 16
Emergency Contacts
You should have emergency information in your phone—you can choose what information you want
to be available, but you should at the very least have one emergency contact listed.
Unfortunately, different versions of the Android OS have different options, so we need to use a
complicated way that should work across most devices— even if the screens look different for every
phone. Your emergency contacts are available even when your screen is locked.
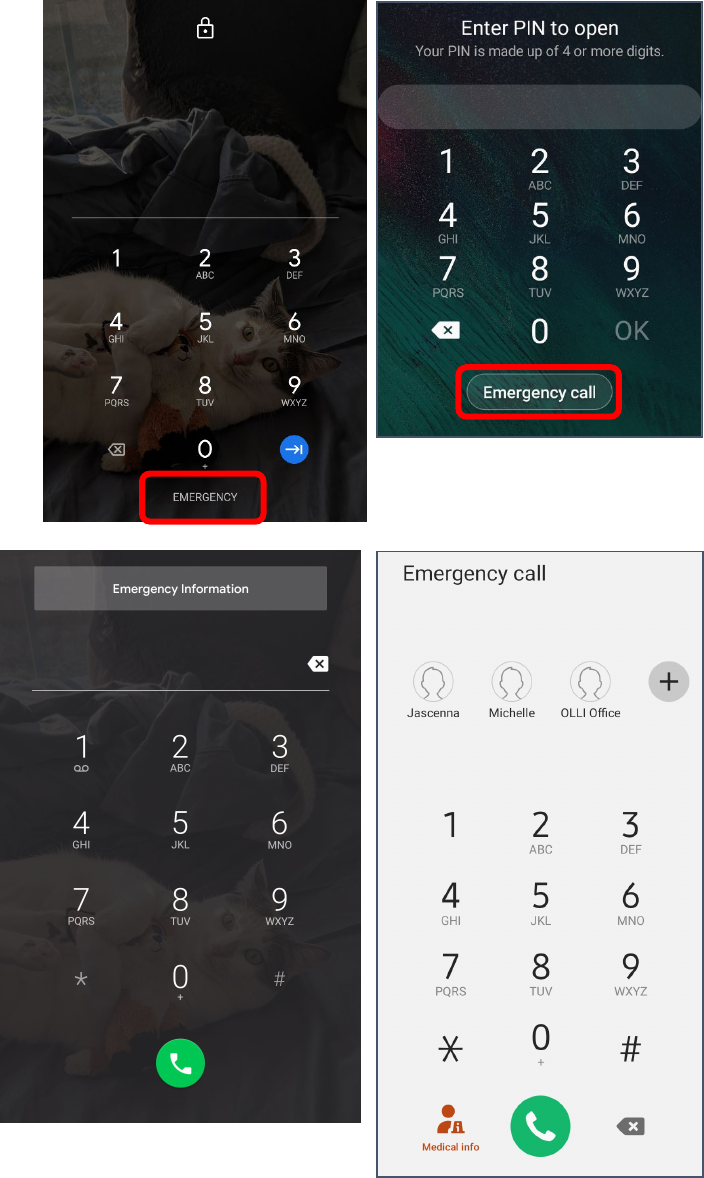
Setting Your Emergency Contacts
1. Open your Contacts (this is not the same as opening the dialer /
keypad and selecting contacts from there). (See page 12)
2. Select a contact.
3. Tap the star to make that individual a Favorite.
4. Return to the home screen.
5. Lock your phone (briefly press the power button).
6. Wake up your phone.
7. In the lower left corner of the screen tap and swipe the phone
icon.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 17
8. Tap the Emergency or
Emergency Call button.
9. The dialer screen is displayed.
Look for a plus sign or button
that allows you to add
someone to your emergency
callers or ICE (In Case of
Emergency) list.
10. You should get a notice that
you need to unlock your
phone to set an emergency
contact. Tap OK and unlock
your phone.
11. Select a frequent or suggested
contact from the list.
12. The next time you open the
emergency dialer, your
contact(s) should be
displayed.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 18
Wireless
If your device has a limited cellular data plan, you will want to connect your phone to wireless as often
as you can.
Although places like coffee shops often have free wireless available for their customers, you should be
extremely careful when connecting to open wireless connections—any information you pass over that
connection could be visible to anyone who cares to look.
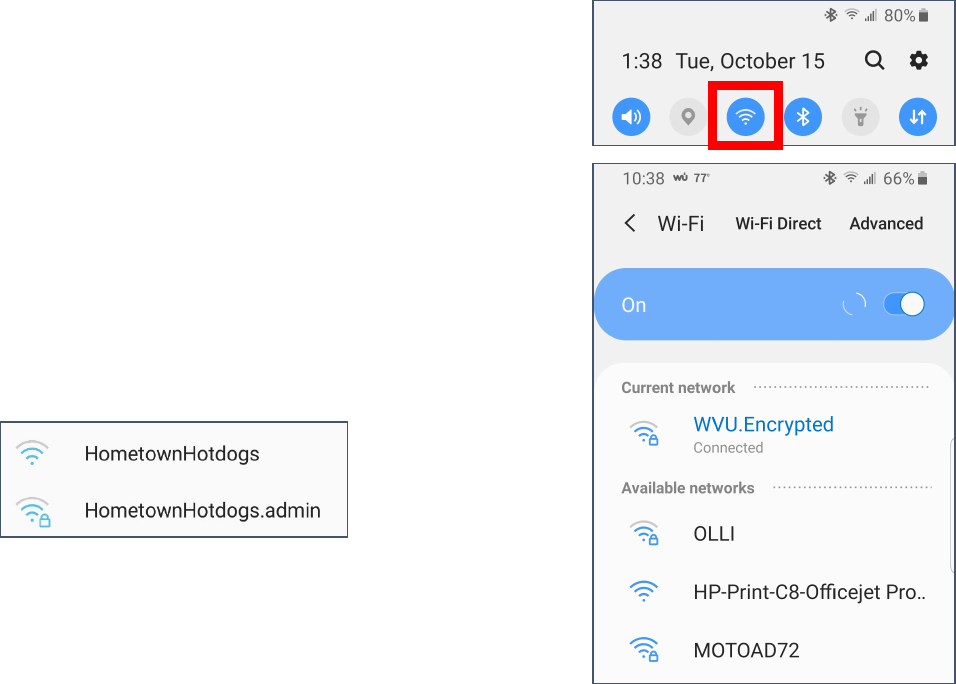
To Turn Wireless Off and On
1. Pull down from the top of the screen to access your Quick
Settings. (See page 3).
2. Tap on the Wireless icon to toggle the wireless on or off.
To Select a Wireless Network
1. Long press on the wireless icon.
2. A list of available networks will appear.
3. Tap on the network you want to join.
4. Enter the password for the network when prompted.
Secured vs Unsecured Wireless Networks
You can tell at a glance whether a wireless network is secured or
unsecured by checking for a “lock” on the wireless icon.
You should also be required to enter a password to access a
secured wireless network.
Please be aware, however, that you should not send personal
information over a public network, even if it is secured.
Texting
Text Messages and Phone Data
There are two different types of text messages: SMS and MMS.
SMS: Short Messaging Service. A brief message that is sent from one phone number to another
phone number. SMS does not use cellular data.
MMS: Multimedia Messaging Service is a kind of text messaging that allows you to send text
messages that contain pictures or audio, as well as messages longer than 180 characters or to multiple
people.
This difference is important because text messages count against your text limit on your cellular plan,
while SMS messages use data. If you do not have mobile data turned on, you will not receive SMS
messages. Additionally, you cannot send text messages to people who do not have a phone number.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 19
Text Messages
Text messages are brief messages sent from one phone number to another. They are
useful because unlike a phone call, they can be asynchronous, are also more likely to go
through during an emergency, use less battery, and will be received even if the recipient
has their phone turned off when you send the message.
Android phones come with a default messaging app, but many people prefer to purchase and use a
third party app, which allows them greater customization and options.
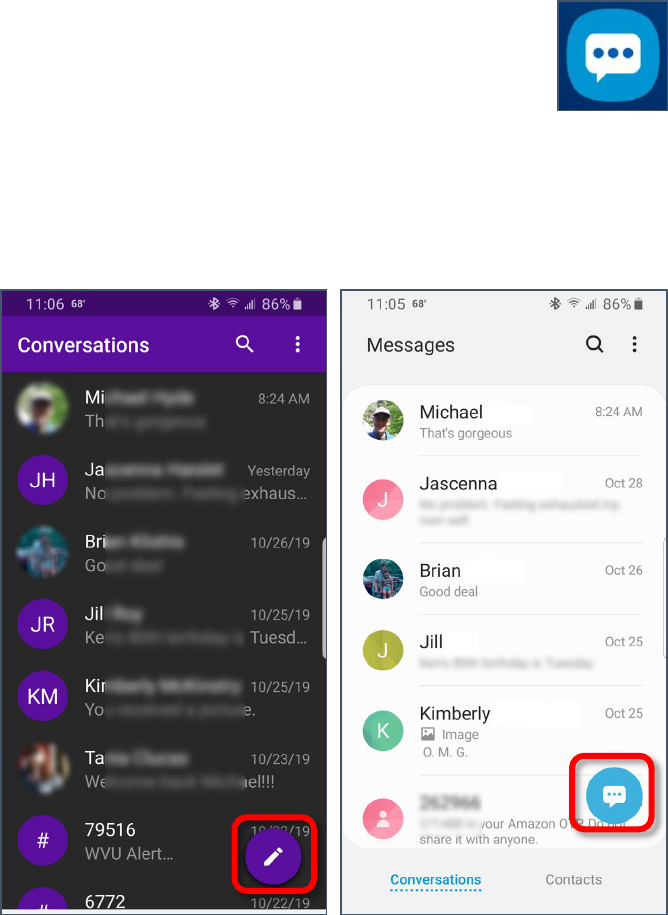
Sending Text Messages
1. Open your texting app. If you are using the default Android app, it should look something like the
above icon.
2. If the person to whom you want
to send a message is at the top of
the list, simply tap the existing
conversation and add your
message.
3. If you don’t see a recent
conversation, or you have never
texted with the person before,
look for the new conversation
icon, usually in the lower right
corner.
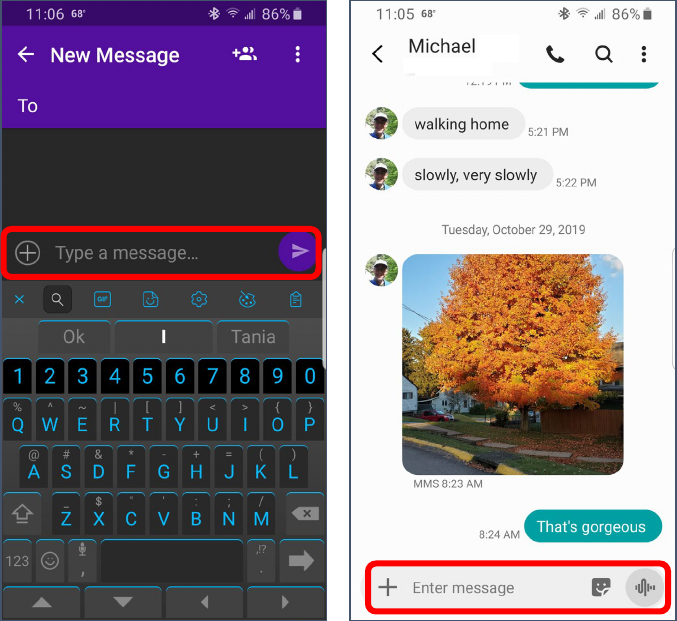
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 20
4. When you tap in the box that
says “Enter message” or “Type a
message” the keyboard appears
so you can enter your message.
5. Once you have completed your
message, tap the Send button at
the end of the text box.
6. For a list of common texting
acronyms, see page 36.
Alternatives to SMS Texting
Texting allows you only to reach people who have cell phone numbers, and generally plans charge
extra for international texting. Many people also have limited texting plans, and the ability to send
text messages over WiFi is an important option. There are plenty of alternatives to regular texting
from Skype to Whatsapp, you just have to make sure that you and the person you want to chat with
are both using the same program.
You can also use Facebook messenger as a messaging app, but for privacy and security reasons it is
NOT recommended. Please see page 36 for a list of alternative programs.
Apps
Apps are programs or software packages (applications) that run on your device’s operating system.
For Android devices, apps are available from the Play Store. You also have the ability to install third
party apps that do not come from the Play story, but this is not recommended until you are quite sure
what you are doing.
Some common types of apps are Email apps, podcast apps, web browser apps, social media apps, and
ebook apps.
Closing and Removing Apps
Closing Apps
1. Tap the Recent Applications Menu button, usually at the lower left of the screen. A list of open
apps appears
2. To close an individual app, click the x beside the app or swipe right on the app.
3. To close all open apps, if available, tap Close All.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 21
To be clear, stopping an app frequently leaves parts of that app still running in the background. To
end all processes of that app, you need to force the app to stop.
Force Stopping Apps
1. Open your device settings. (Typically available from the list off all applications or by pulling down
from the top of the screen to open the system tray, and tapping the gear icon.)
2. From the list of available settings, choose Apps or Applications. (Depending upon your phone.)
3. Scroll through the list to find the specific app you want to close and/or keep from running in the
background.
4. Towards the top of the screen, tap the Force Stop button.
5. The device asks if you are sure you want to do this, tap Force Stop.
Uninstalling Apps
1. Open your device settings. (Typically available from the list off all applications or by pulling down
from the top of the screen to open the system tray, and tapping the gear icon.)
2. From the list of available settings, choose Apps or Applications. (Depending upon your phone.)
3. Scroll through the list to find the specific app you want to close and/or keep from running in the
background.
4. Towards the top of the screen, tap the Uninstall button.
5. In the verification window, click OK to uninstall the app.
Google Play Store
Most people will search for and install new apps from the Google Play store.
There are free apps and there are paid apps. Unless an app is open source or you are
certain how the information is going to be used, I recommend paying for the apps you
install on your device. In some cases there aren’t paid options, just be aware that free apps are highly
likely to be invading your privacy and / or making money off your data.
Finding and Installing New Apps
1. Open the App Store.
2. At the top of the page, tap in the box where it says “Search for
apps &…”
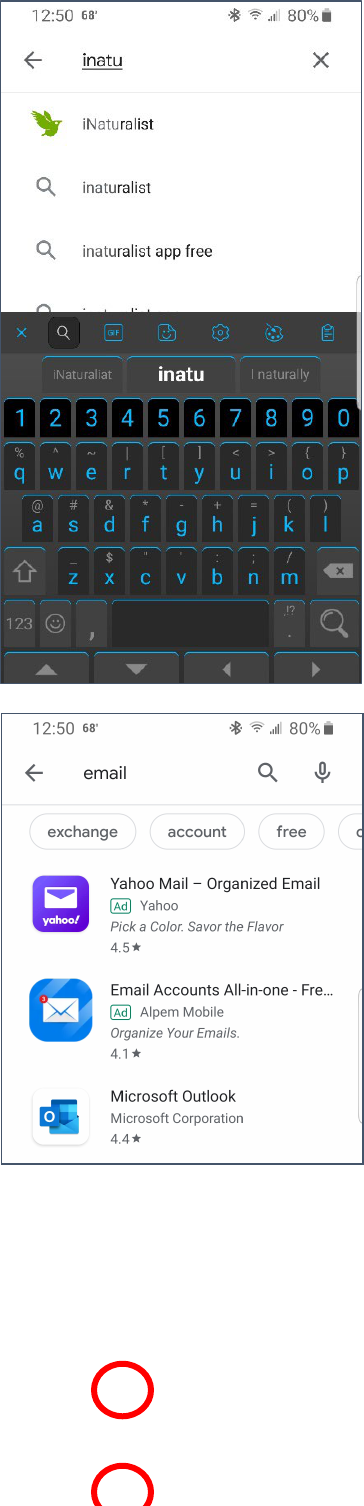
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 22
3. Begin to type in the name of the app you are looking for; a list
of matching apps. Tap on the app you want to check.
4. A list of apps matching your search term is displayed.
5. Note that the first apps listed are often ads.
6. Tap on an app to learn more about it.
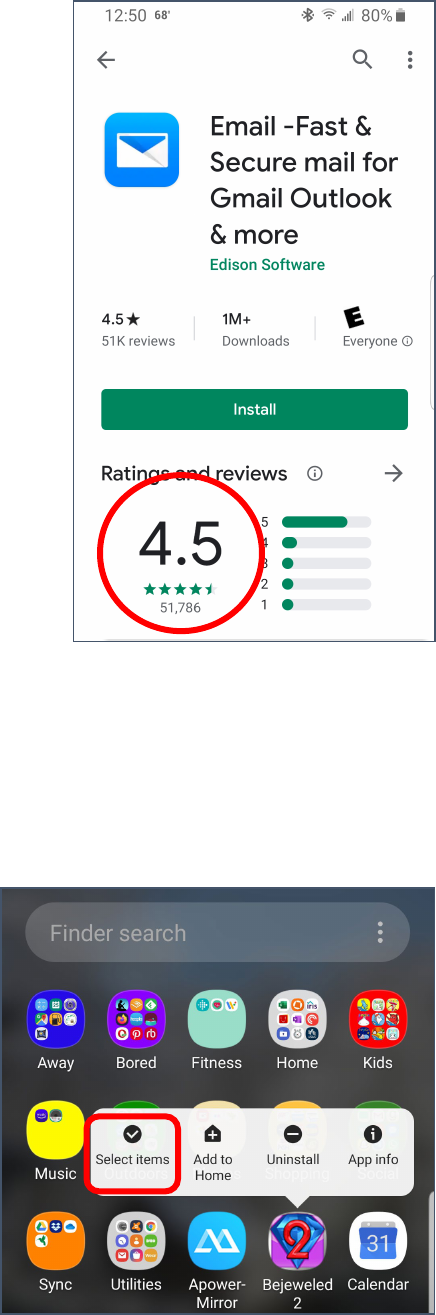
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 23
7. Pay attention not just to the rating of the app (4.5 / 5) but also
to how many people have reviewed the app. A rating of 4 from
50k people is more useful than a rating of 5 from 2 people.
8. If you decide you want the selected app, tap Install.
9. The app will be installed on your device (speed of download
and install depends upon your internet connection) and the
app should be available on one of your home screens and from
the app store.
Folders
Folders can be used to organize your apps—putting similar apps in one place and allowing you to have
a single home screen or app screen. For some people folders are the best thing ever, but for others
folders can make it harder to find what you’re looking for. There is not judgement as to whether you
should or should not use folders—just use your device in the way that makes it easiest for you to find
things.
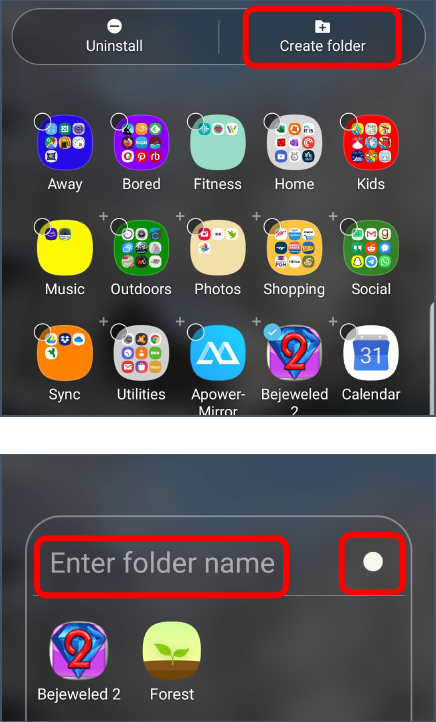
Creating a Folder
1. From your home screen or app drawer, long press on
an icon that should belong in your new folder.
2. Tap Select items.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 24
3. Tap a second item.
4. At the top of the screen tap Create folder.
5. Tap in the Enter folder name area to create a name
for the folder.
6. Tap the white dot to set the background color for the
folder.
7. Tap away from the folder area to complete the steps.
Adding Apps to a Folder
1. Long press on the icon you want to move.
2. While still pressing, drag the icon over the folder.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 25
Camera
One of my favorite things about cell phones is that I always have a camera in my pocket.
Most newer cell phones have cameras comparable to stand-alone digital cameras, and
also have the ability to edit images and immediately share them.
Using Your Cell Phone Camera
1. Using a soft cloth (ie the hem of a t-shirt),
briefly wipe off the camera lens.
2. Tap the Camera icon.
3. Tap on the screen on the area upon which
you want to focus.
4. Tap the white circle icon to take a picture.
Taking a Selfie
1. Using a soft cloth (ie the hem of a t-shirt),
briefly wipe off the camera lens.
2. Tap the Camera icon.
3. Tap the Front / Rear Camera Toggle
icon.
4. Holding the device as still as possible, tap
the White Circle icon to take a picture.
The Android operating system gives you a
variety of setting options. The more important
options are for picture size, save options,
location tags, and storage location.
Camera Settings
1. Tap on the Settings icon.
2. Scroll through the settings and change the settings as
desired.
Settings
Flash
Timer
Selfie
Toggle
Camera
Modes
Prev.
Photos
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 26
Photos
The default app for viewing your images may depend upon your phone make, however,
Google’s Photos app is available to all Android Devices. And you can also choose a
different photo gallery app.
Icons
Sharing
Delete
Albums
Individual Photos
Photo Settings
1. Open your Photo Gallery. We are going to use Google’s Photo App
in these examples.
2. Along the bottom of the screen, you can switch views between
Photos and albums.
3. The three parallel lines or dots in the top left corner allow you to
access your settings.
4. Scroll down the menu until you see the gear icon and Settings.
• Backup and sync: Allows you to automatically sync all
your photos to Google Drive
• Free up device storage: Allows you to automatically
delete images that have been saved to your Google account.
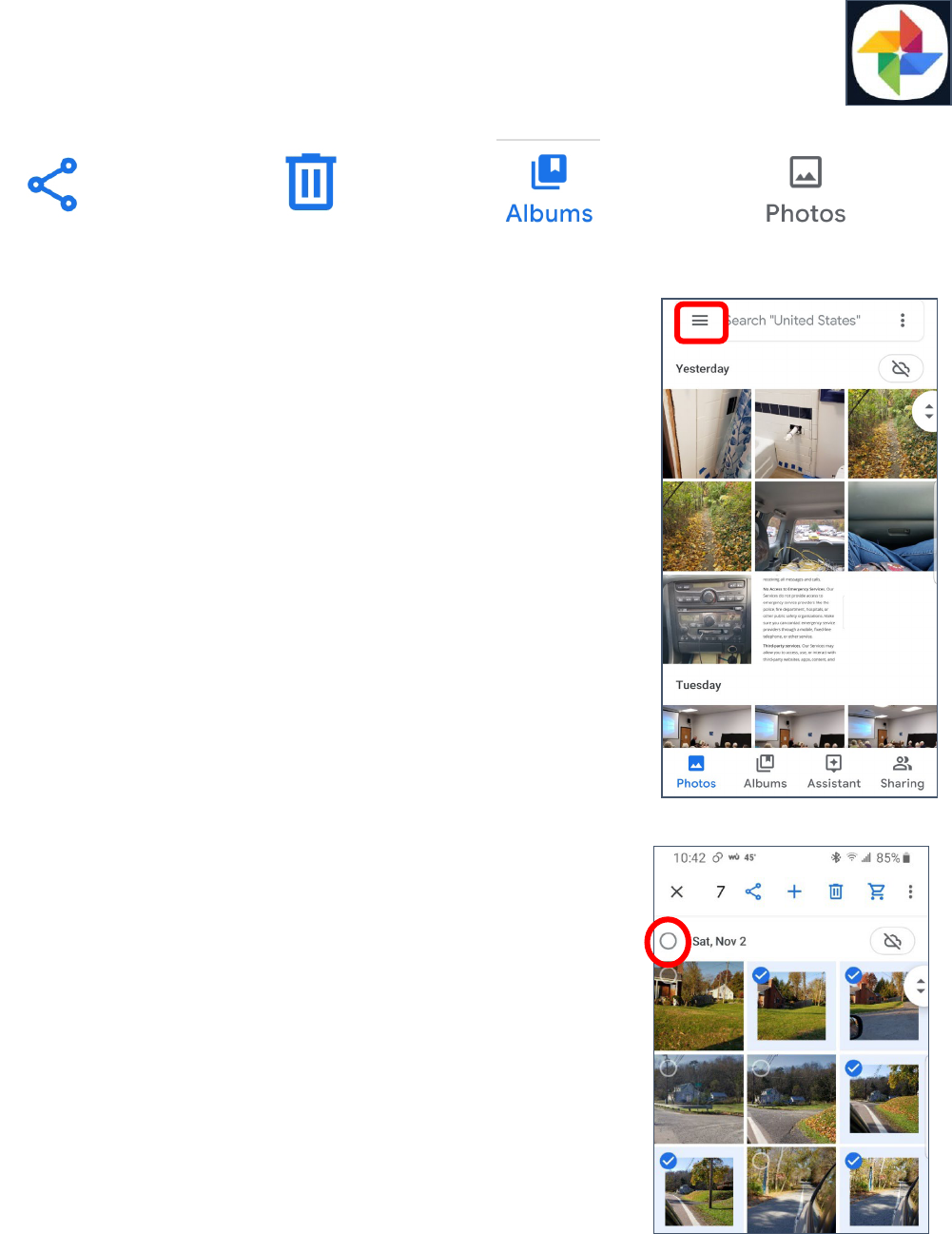
Selecting Photos
1. Tap a single photo to view that image.
2. Tap and hold a single photo to select it.
3. Once one photo has been selected, you can tap other photos to
select them as well.
4. You can select all the photos from a selected date by tapping the
circle beside the desired date.
5. Different items appear once a photo has been selected. The trash
can icon allows you to Delete the selected items. The “less-
than” icon (<) allows you to Share the selected images. The
“plus” (+) icon allows you to move the pictures to a folder.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 27
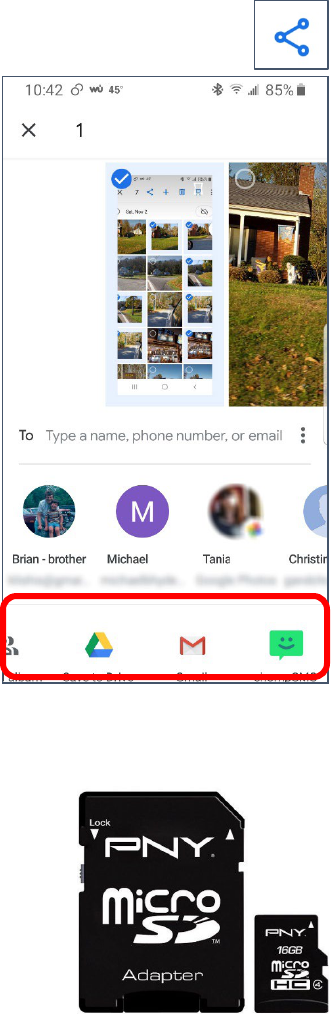
Sharing
Sharing is used both for sending a file to someone else and to copy a file to a cloud service.
Sharing Photos
1. Select one or more images.
2. Tap the Sharing icon.
3. Along the bottom of the screen, you can scroll to the right to
select the app through which you want to share the images.
Common apps to use for sharing are email, cloud drives, and
texting apps.
4. Once you select the desired app, it will walk you through the
process of sharing the picture(s).
SD Cards
Many Android phones have the ability to use micro-SD cards. A micro-SD
card is a smaller SD card that is used in lightweight devices like phones. An
SD card can allow you to double or even quadruple the amount of memory
on your phone. This expanded storage allows you save more files like songs
and photos to your device, and can also help extend the life of an older
phone with less internal storage.
Many—but not all—apps can be transferred to an SD card, as can storage of
pictures, music, and books.
Checking for an SD Card
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Search for Storage.
3. Scroll down until you see SD Card Storage.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 28
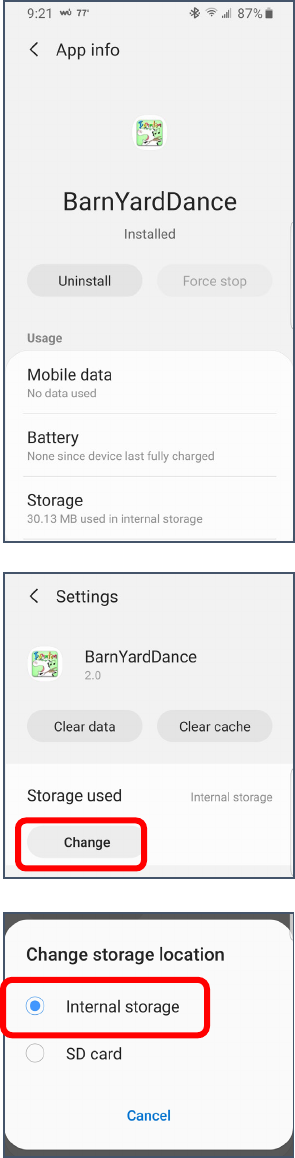
Transferring Apps to the SD Card
1. Open your Settings. (See page 3)
2. Search for and open Apps.
3. Scroll through your list of apps until you find an app you want to
move to the SD card. Tap that app.
4. The information for that specific app appears. Scroll down and tap on
Storage.
5. If the app can be moved (some can’t) there will be a Change button
available. If it says Internal storage, tap the Change button. If it says
SD card, you’re done.
6. In the box that opens, tap Internal Storage.
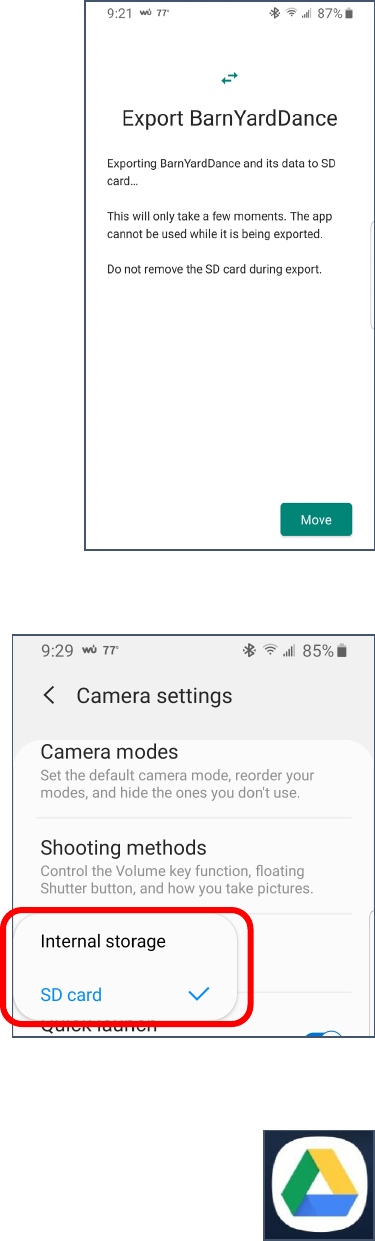
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 29
7. Tap Move to complete the move.
8. Wait patiently.
Saving New Pictures to the SD Card
Another way to free up space on your device is to save new
pictures you take directly to the SD Card.
Changing the Save Location for New Pictures
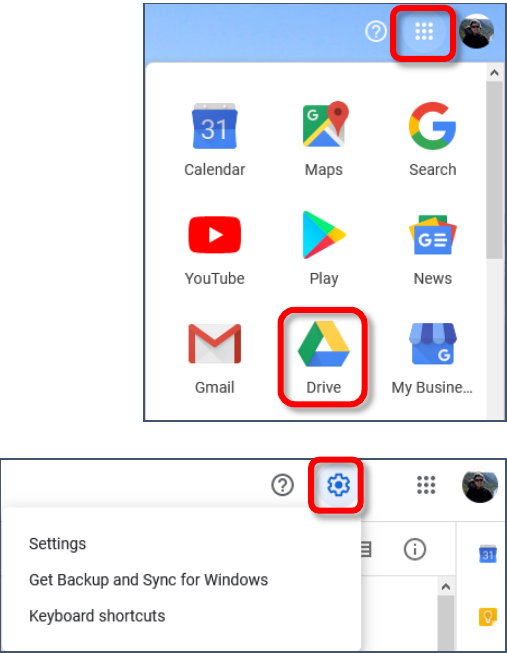
1. Open the camera app.
2. Tap for the “gear” or Settings icon.
3. Scroll down until you see Storage location. If it says
Internal Storage, tap on Storage location and select SD card.
4. If it already says SD Card, you are good to go!
Google Drive
Google Drive (also called Backup and Sync from Google) is a cloud storage service that
allows you to copy files easily from your phone to a computer or other device, and to
share then with friends and family.
I use Google Drive to copy pictures from my phone to my computer. I “share” pictures from my
photos to Google Drive. Once the pictures are available on my computer, I move them from google
drive into a local folder. The original picture remains on the computer, but once you move the copy
from Google drive, that copy now resides on your computer.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 30
One important thing to remember is that when you move something (like a photo) from Google drive,
it is removed from Google Drive on ALL locations.
Setting up Google Drive on Your Computer
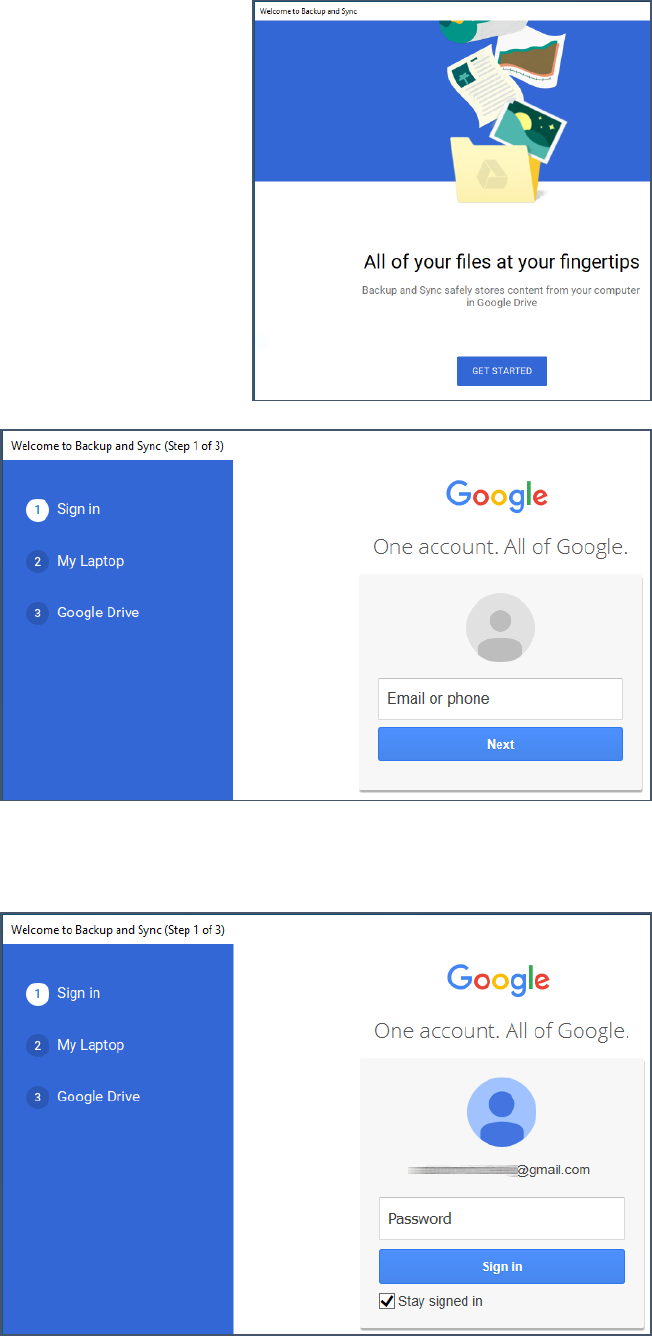
1. Log into your google account. If you already have gmail open,
you’re already logged in.
2. At the top right corner of the window, click the Google Apps
icon (the square of squares).
3. Scroll through the drop down menu until you can click on the
triangle Drive icon.
4. A new window displaying your Google Drive files
opens.
5. Click on the Settings (gear) icon.
6. From the drop down menu select Get Backup
and Sync for Windows.
7. In the Personal Backup and Sync area, click
Download.
8. After reading the Terms of Service, click the
Agree and download button.
9. Save the file.
10. If you are not prompted to do so, double click on the “installbackupandsync” installer to begin the
installation process. (This file is most likely saved to your Downloads folder).
11. Once the program has installed, you will be walked through a series of prompts to finish setting up
the program.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 31
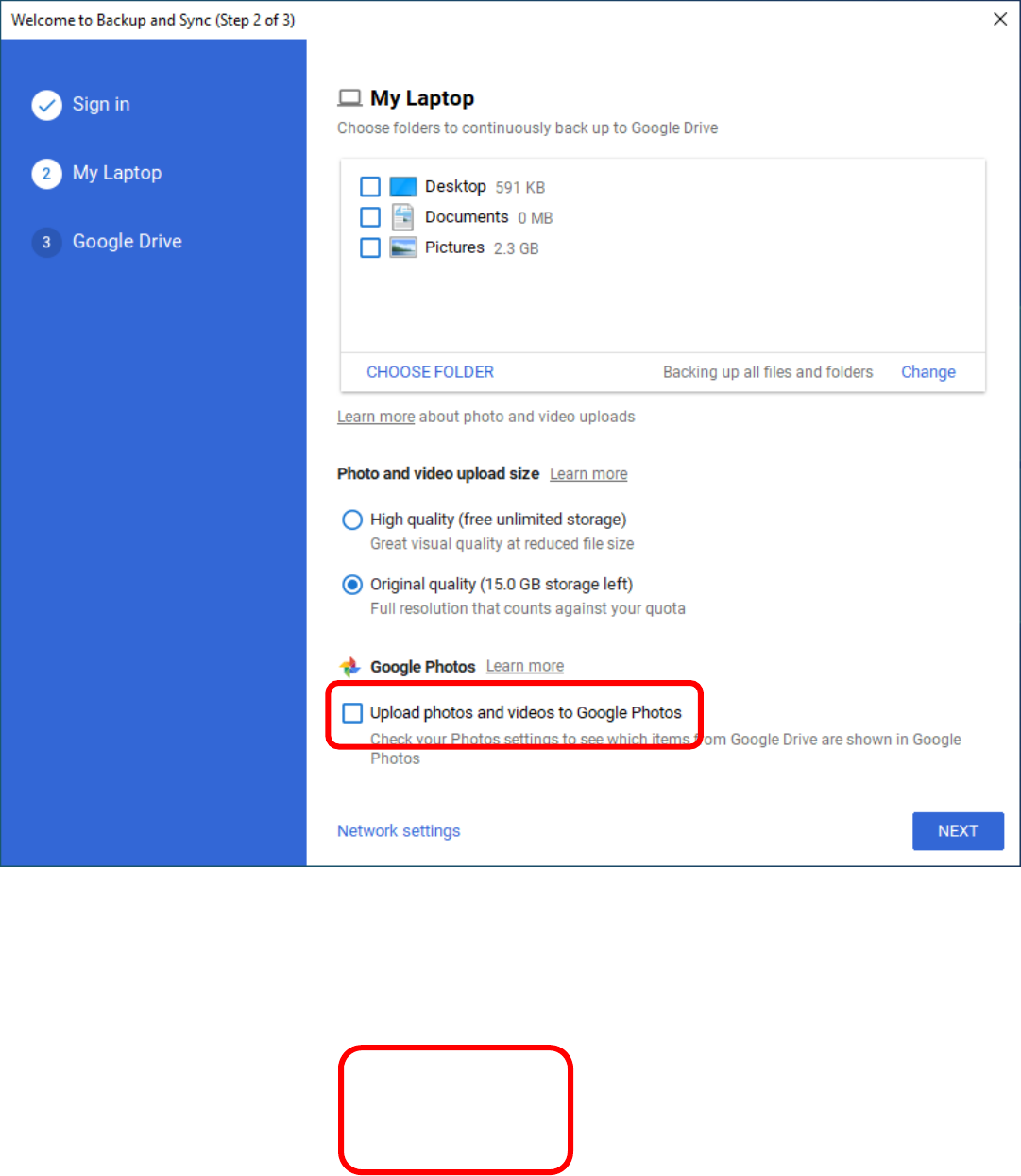
Setting Up Google Drive on Your PC
1. Google Drive should automatically launch. If it does not, it
can be found in the Windows Menu under Backup and
Sync from Google.
2. In the first window that appears, click Get Started.
3. Enter your google user name (the first part of your email address).
4. Click Sign In.
5. Enter your password for the
account.
6. Click Sign In.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 32
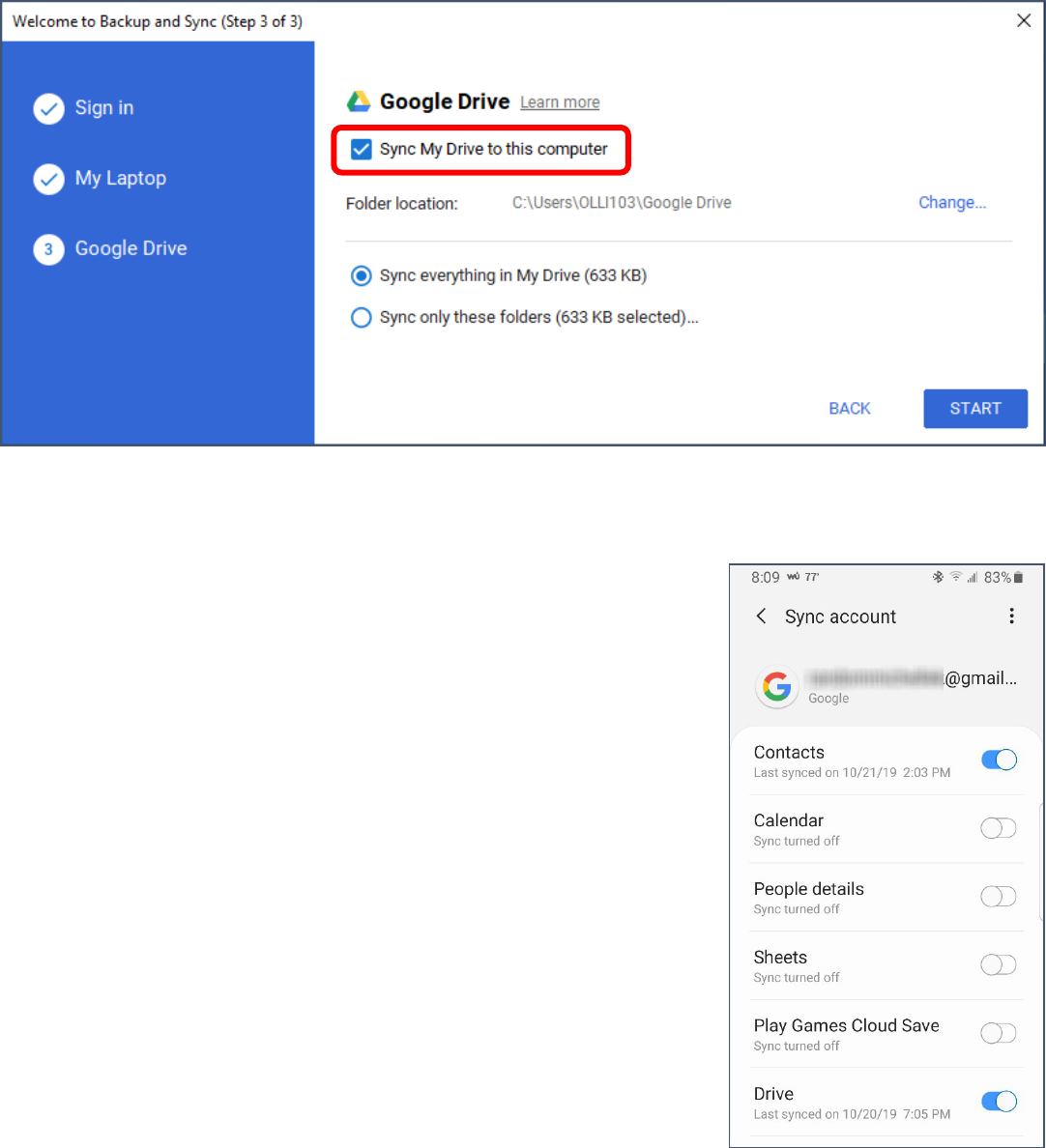
7. In step 2 of 3 you are going to set up what files you want to sync. The following are my
recommendations—you can choose other options or changes these options at any point in time. At
the top of the window, deselect Desktop, Documents, and Pictures. The reason for this is
because this may quickly fill up your drive AND you may have personal files you do not want to be
saved to the cloud in these locations.
8. Towards the bottom of the screen deselect Upload phots and videos to Google Photos.
Again, this is both for privacy and to save space.
9. Click Next.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 33
10. Leave Sync My Drive to this computer ticked.
11. Click Start.
Backup and Sync
Backups and sync can keep you from losing important information
(like your address book) if your phone is lost or destroyed. If
something is important, you should back-up or sync it to the cloud.
Backup and sync can be easily linked to your google account
(although you do have other options).
You’ll access these options through Settings and then Accounts (or
Accounts and Backup) and then select Accounts. You can then scroll
through the list of all your accounts, select a single account (google
accounts should have a multi-color G icon) and select what items you
want to sync.
Accessing Backup and Sync
1. Open your Settings.
2. Scroll down to and tap on Accounts and backup or Accounts.
3. Tap on Accounts.
4. You should see a list of all accounts that have the ability to sync.
The easiest sync to set up is to use your existing Google account.
Select the account you want to use.
5. Under that account, look for “Sync account”.
6. Toggle the various settings to select what you do—and do not—
want to sync.
You should also go through all other accounts that are synced to your device.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 34
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a near-field wireless technology that allows communication between devices
over a very short distance.
Some common Bluetooth devices are speakers and headphones, and wireless mice, but
Bluetooth can also be used to transfer files between devices.
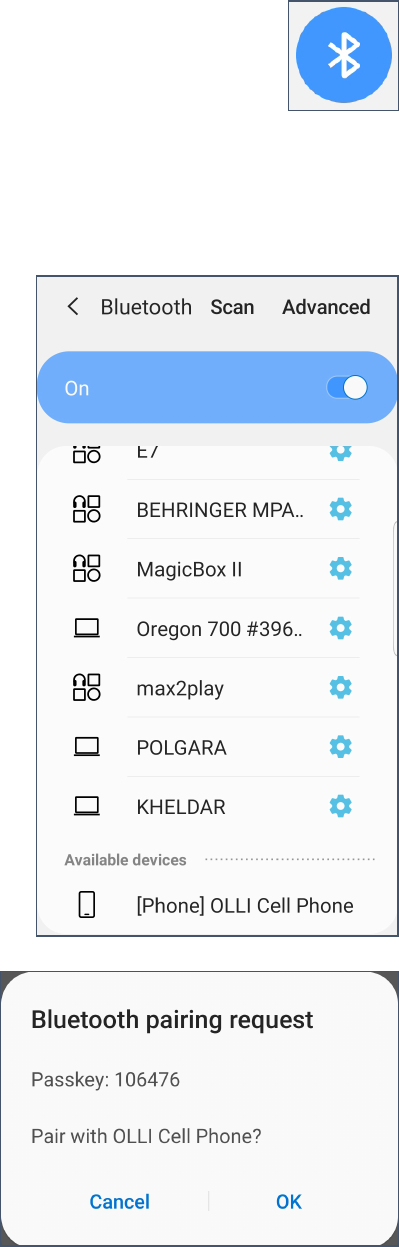
Adding a Bluetooth Device
1. Open your Settings and search for Bluetooth.
--OR—
Open your Quick Settings and long press on the Bluetooth icon.
2. A list of available and paired devices is listed at the top. Scroll
down to the bottom of the screen for Available devices.
3. If the device to which you want to connect is not listed, tap
Scan.
4. When the device you want to link to appears, tap it.
5. If the devices can pair, you may receive a message for a
pairing request. Click OK.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 35
Smart Lock
Once certain devices have been paired (such as smart watches or headphones) they can be set as Trust
Agents that keep your device unlocked while in range.
Setting Up Smart Lock
1. Open Settings and search for Smart Lock.
2. You will be prompted to enter your passcode.
3. Select Trusted devices.
4. Scroll down and select Add trusted device.
5. Select a currently connected device.
Email
Android systems come with a default Email app. You can also download a different email
app (like Gmail or Outlook) to use on your device. All apps will require you to know basic
information about your account, such as your username (the part of your email address
before the @ sign) and password.
If you use a common email provider, like hotmail or yahoo, the app will automatically fill in any other
information needed to retrieve your messages from the server.
Music
For many people, cell phones have replaced their portable music players (after all, a cell phone is
easier to slip in your pocket than a Walkman or boom box!).
Some phones will come with apps for streaming services (like Spotify or Pandora) pre-installed. You
can also use “google play music” as an app to play songs you have downloaded to your device.
There are multiple ways to get music to your device. You can download purchased music from a cloud
service like Amazon Music or Apple Music, or you can rip CDs and transfer those files via a micro SD
card or Bluetooth or USB cable.
Podcasts
Podcasts are typically an audio series put out on a regular basis that can be downloaded by
subscribers automatically. Podcasts can be on any topic, from sports to politics to stories to book
recommendations.
There are a wide variety of podcast apps available, including one native to Android.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 36
Texting Apps that Work over WiFi
Whatsapp: https://www.whatsapp.com/
Telegram: https://telegram.org/
Snapchat: https://www.snapchat.com/
Skype: https://www.skype.com/en/
Signal: https://signal.org/
Hangouts: https://hangouts.google.com/
Cloud Services
Box: https://box.com
Dropbox : https://www.dropbox.com
Google Drive: https://www.google.com/drive
iCloud: https://www.icloud.com
One Drive: https://onedrive.live.com
SugarSync: https://www.sugarsync.com/
Sync.com : https://www.sync.com
Android Voice Commands
https://support.google.com/accessibility/android/answer/6151848?hl=en
Setting ICE Contacts on Samsung Galaxy S8 and S9 https://medium.com/@n.craig_62483/setting-
ice-contacts-on-samsung-galaxy-s8-and-s9-35b4072221c7
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 37
Texting Acronyms
AF: As (naughty word)
AFK: Away from Keyboard
BTW: By the Way
B/C: Because
BFF: Best Friends Forever
BRB: Be Right Back
CU: See You
CYT: See You Tomorrow
DGMW: Don’t Get Me Wrong
EOD: End of Discussion
EOM: End of Message
F2F: Face to Face
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
(pronounced fak to rhyme with pack)
FREX: For Example
FTW: For the Win
FWIW: For What It’s Worth
FYI: For Your Information
GR8: Great
HTH: Hope This Helps
ICYMI: In Case You Missed It
IDC: I Don’t Care
IDK: I Don’t Know
IIRC: If I Remember/Recall Correctly
IMHO: In My Humble Opinion
IMO: In My Opinion
IOW: In Other Words
IRL: In Real Life
J/K: Just Kidding
L8R: Later
LOL: Laugh(ing) Out Loud
MYOB: Mind Your Own Business
noob / n00b: Newbie
NNTR: No Need to Reply
NOYB: None of Your Business
NP: No Problem
NRN: No Reply Needed
NSFW: Not Safe for Work
OMG: Oh My God
OMY: On My Way
OTOH: On the Other Hand
OT: Off Topic
OTP: On the Phone
ROTFL: Rolling on the Floor Laughing
RTFM: Read the Fantastic Manual
RU: Are You
SFLR: Sorry for Late Reply
SO: Significant Other
TBC: To Be Continued
THX: Thanks
TIA: Thanks in Advance
TL;DR: Too Long Didn’t Read
TMI: Too Much Information
TTYL: Talk to You Later
TUVM: Thank You Very Much
TYT: Take Your Time
UR: You Are / Your
w00t / W00T: Hooray! Yay! Yippee!
W8: Wait
WFM: Works for Me
WRT: With Regard To
WTH: What the H(eck)
WTF: What the (naughty word)
YMMV: Your Mileage May Vary
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 38
Emoticons
(.V.)
Alien
O:-)
Angel
X-(
Angry
~:0
Baby
:-D
Big Grin
(*v*)
Bird
:-#
Braces
</3
Broken
Heart
=^.^=
Cat
*<:o)
Clown
O.o
Confused
B-)
Cool
:_(
Crying
:'(
Crying
\:D/
Dancing
*-*
Dazed
:o3
Dog
#-o
Doh!
:*)
Drunk
//_^
Emo
>:)
Evil Grin
<><
Fish
:-(
Frown
:(
Frown
:-(
Frowning
=P
Frustrated
:-P
Frustrated
8-)
Glasses
$_$
Greedy
:->
Grin
=)
Happy
:-)
Happy
:)
Happy
#
Hashtag
<3
Heart
{}
Hug
:-|
Indifferent
X-p
Joking
:-)*
Kiss
:-*
Kiss
:*
Kiss
(-}{-)
Kissing
XD
Laughing
=D
Laughing
Out Loud
)-:
Left-
handed
Sad Face
(-:
Left-
handed
Smiley
Face
<3
Love
=/
Mad
:-)(-:
Married
@
Mention
<:3)~
Mouse
~,~
Napping
:-B
Nerd
^_^
Overjoyed
<l:0
Partying
:-/
Perplexed
=8)
Pig
@~)~~~~
Rose
=(
Sad
:-(
Sad
:(
Sad
:S
Sarcastic
:-@
Screaming
=O
Shocked
:-o
Shocked
:-)
Smile
:)
Smile
:-Q
Smoking
:>
Smug
:P
Sticking
Tongue
Out
:o
Surprised
:-J
Tongue in
Cheek
:-&
Tongue
Tied
=-O
Uh-oh
:-\
Undecided
:-E
Vampire
=D
Very
Happy
;-)
Winking
;)
Winking
|-O
Yawn
8-#
Zombie

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 39
Technology Glossary
Add-on
An accessory piece of software designed to increase the capability of the software to which it is
appended.
Address Book
See Contacts
Alexa
Amazon’s virtual assistant.
Algorithm
A set-of rules to be followed in calculations or problem-solving operations. Algorithms are frequently
used to manipulate data sets.
Android
Googles mobile operating system, built on open source software.
Anti-Virus
A program that protects you from malicious software. Most anti-virus programs have options for
purchasing additional security measures such as firewalls, email scanning, etc.
App
Short for Application.
Apple ID
This is the username and password that you create with Apple to link a specific device to your Apple
account. If you have an iPad and an iPhone, you use the same Apple ID with both of those devices.
Apple
Technology company that designs and develops hardware and software.
Application
An application is a piece of software that lets your device do something, like play music or give
directions. An application is the same thing is a program.
Autocorrect
Auto correct is when your phone automatically changes what you were typing to what it thought you
wanted to type.
Autoplay
When you visit a website and music or video starts playing without asking.
Backup
A copy of computer data that is taken and stored somewhere else, to be used in the event of data loss.
BCC
Blind carbon copy. Secretly send a copy of the message to someone else. The primary recipient cannot
see that this person received the message.
Blockchain
Also Block Chain. A list of records (blocks) linked using cryptography. These records are a
cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Blockchains are
generally used on a peer-to-peer network. Data in one block cannot be altered without changing all
other blocks.
Bluetooth
A wireless technology that allows data to be shared over short distances using short-wave UHF radio
signal.
Boolean
A system of logical propositions. Common Boolean operators: AND, OR, NOT, “ “, ( ) . Based on the
work of George Boole.
Browser Add-on
See Browser Extension.
Browser Extension
A small software module that is used to customize a web browser.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 40
Browser Hijack
Where a malicious piece of software modifies a web browser’s settings without your permission.
Browser
Short for Web Browser.
Brute Force Attack
Where a hacker tries many passwords for passphrases in an attempt to break into your account. The
longer your password (or passphrase) the harder it is for someone to use this kind of attack to break
into your account.
Byte
A unit of digital information that consists of eight bits. A byte is the number of bits used to encode a
single character of text.
Cache
Temporary storage space that allows your computer to quickly bring up information, such as
previously viewed web pages.
Cambridge Analytica
A British political consulting firm that used misappropriated digital assets, data mining, and other
processes to influence political elections around the world.
CC
Carbon copy. Send a copy of the message to someone else. The primary recipient can see this person
received the message.
Cellular Data
The connection your cell phone makes to a cell tower that allows you to do things like surf the
internet, download emails, and send SMS messages.
Cloud
Storage that is physically somewhere other than where you are. Cloud storage is generally accessible
from multiple devices, because those files are stored on a hard drive that belongs to a company that
hosts the cloud service. Cloud storage is like a self-storage unit for your electronic files, except you can
access your stuff from anywhere.
Codec
A device or program that encodes/decodes a data stream, such as an audio file, for storage.
Contacts / Contact List
A collection of screen names and the various data associated with them, such as email addresses and
telephone numbers.
Cookie
A piece of data that a website saves on your computer. Cookies were designed to save user
information such as preferences or logins, but can sometimes be read by third parties. Cookies are
also used to collect browsing data long-term.
Cortana
Microsoft’s virtual assistant.
CPU
Central Processing Unit. The bit of a computer or electronic device that processes information.
Cryptocurrency
A digital asset that uses strong cryptography and is designed to work as a form of money. They used
decentralized control, or a public financial database to keep track of who owns what.
Cryptography
Greek for “hidden writing”, it is the study of secure communication—creating protocols to keep third
parties from reading private messages.
Data Breach
The release of secure or private information. A data breach can be accidental or malicious, such as
when an individual hacks into a system to steal information.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 41
Database
An organized collection of information. Complicated databases link information between multiple
tables allowing for analysis of the contained information. An address book is a basic database.
Denial of Service Attack (DOS)
A cyber-attack where the malefactor seeks to make a network resource (such as a website) unavailable
by flooding the target with requests or visits.
Directory
A system that catalogs / organizes computer files.
DNS Hijacking
Where a malefactor redirects visitors from a valid website to a different destination—often one that
exists to steal data.
Domain Name
The string of text that identifies a place on the Web. A basic domain name is a word or abbreviation
followed by a period followed by the domain extension: wvu.edu
Domain
The sometimes arbitrary grouping that designates what a website does or where it is based. The most
common domains are .com .net .edu and .org. The domain is what you should check first when you
want to verify the authenticity of a website.
Download
To move data and files from the internet or a server to your computer or mobile device.
DVD
Digital Video Disc / Digital Versatile Disc. A digital optical disc data storage system.
Email Header
The portion of an email message that contains the routing information. The header can be used to
help determine if a message is fraudulent.
Email
Email is an electronic letter sent from one email address to another email address. Email addresses
always have an @ (at sign) in them. Sending an email on your phone requires the use of cellular data.
Each email address is unique, and email addresses are often used as unique identifiers or login
credentials by databases.
Emoji
Small images used to represent emotions, ideas, or expressions.
Emoticons
Representations of facial expressions using keyboard characters. These are used to portray moods or
feelings. For example, a smiling face could be :) or
Encryption
The encoding of data so that only authorized persons or devices can read/view the information. The
stronger the encryption, the more unlikely it is that a malfeasant could decode the intercepted data
through a brute force attack.
EULA
End-User License Agreement. The legal contract between a software vendor and the user of that
software. It specifies the rights and restrictions which apply to the use of the software.
External Storage
Devices that store data outside of a computer or other electronic device. They are often removable,
such as USB thumb drives.
Facebook
An online media and networking company.
Facial Recognition
Technology capable of identifying or verifying a person from a digital image. Facial recognition can be
used to unlock an electronic device.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 42
File Extension
Also called a filename extension or file type, is the identifier suffix for a computer file name, and tells
you the kind of program needed to open the file. By default, these extensions are hidden, but can still
be used in search.
Firewall
A security system that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic to prevent unauthorized
access to a system.
Folder
See Directory.
Follow
Choose to see another user’s posts in their content feed.
Force Stop
A way to completely stop an app that is running in the background. An app that has been closed may
still have bits active and collecting data.
GB
Gigabyte. A computer memory unit equal to 1000 megabytes. The prefix giga means 10
9
.
Google
A technology company that specializes in services and products related to the internet.
GPS
Global Positioning System is a piece of hardware that allows a device to contact a satellite to
determine the location of the device in latitude and longitude. On most devices, software makes these
data points usable to the end user by placing them on a map.
Hardware
The electronic components of a device; the bits you can touch. A cell phone, a keyboard, and a CPU
are all hardware.
HDR
High Dynamic Range. A photographic process where a camera takes multiple pictures at different
exposures and combines them into a single image—this allows all areas of your image to be well-
exposed, but can also look unreal if used too much.
Home Screen
The main screen of a computer or mobile device. Home screens are typically personalized by the user
so that no two home screens will look alike.
Hotspot
A type of Wireless Access Point. A device that allows you access the internet from a public place.
Hotspots are generally open and unsecured and you should assume any data you submit is visible to
people with ill-intent.
Hover text
When you hold your cursor over a hyperlink, the document should display the URL for that link. This
allows you to verify links.
http
Hypertext Transfer Protocol is how data is moved between a website and an end user.
https
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (Secure) is an encrypted form of http. This protects against interference
or snooping by third parties.
iCloud
Apple’s cloud service.
Icon
A graphic representation of a program, file or function.
Information Security
The protection of data and the mitigation of risks, generally on computer networks.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 43
Install
A process that writes the code used to run the program (application) onto the hard drive of your
device. Installing a piece of software embeds it into the device and allows it to work.
Internet
A system of inter-connected computer networks.
iOS
Apple’s mobile operating system.
iPad
Apple’s tablet computer, running iOS.
iPhone
Apple’s cellular phone, running iOS.
iPod
Apple’s music player. The iPod is general similar to an iPhone, only without cellular service.
ISBN
International Standard Book Number. A numeric commercial book identifier that is unique for every
edition and variation of a book.
iTunes
Apple’s music service.
Keylogger
Keystroke logger (also keyboard capture). A piece of hardware or a software program that can record
every key struck on the keyboard.
Location Services
Information from GPS, wireless access points, cell towers, and Bluetooth devices that helps your
phone know where you are.
Lock Screen
The opening screen or interface of an operating system. A lock screen keeps unauthorized users from
accessing the data and information on a device.
Lossless Compression
A form of data encoding that maintains the original quality of the file but at the cost of having a large
file size.
Lossy Compression
A form of data encoding used to reduce file size at the cost of data quality.
Messenger
An app that allows users to send text messages and images to other users in a system.
Metadata
A data set that give you information about other data. A card catalog contains metadata.
Micro-SD
Micro-Secure Digital Card. Smaller size SD card, used in phones and lightweight devices. Comes with
an adapter that allows for the transfer for files from a portable device to a computer.
MMS
Multimedia Messaging Service is a kind of text messaging that allows you to send text messages that
contain pictures or audio, as well as messages longer than 160 characters or to multiple people.
Mobile Carrier
A wireless service provider that allows users to connect portable devices (such as phones) to the
internet through a cellular service.
Mobile Data
Wireless internet access through a cellular data connection.
Network
A group of computers connected for the purpose of sharing resources. A network can be as small as
two computers or as vast as the Internet.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 44
News Feed
The main page of Facebook, where you see content posted by users you have chosen to follow. These
content can be text or images.
Notification
A message displayed by an electronic device to provide an alert, reminder, or other communication.
Online Chat
Real time communication over the internet through (generally short) text messages.
OS
An Operating System is the base upon which software and apps are added. An Apple device generally
uses iOS (iPhones) or macOS (laptop computers). PCs typically used the Windows OS, but there are
other operating systems, such as Linux that can be installed. Non-Apple cell phones frequently use
some form of the Android OS. How your device looks and works is dependent upon the operating
system installed.
P2P
Peer-to-Peer
Passcode
This is the secret code to get into a specific device. If you have an iPhone and an iPad, they can have
different passcodes. You can sometimes use a fingerprint instead of a passcode to get into a device.
Password Manager
A program that stores electronic passwords.
Password
The secret code to access a restricted resources. Passwords are usually required to use a minimum of
eight characters, and contain special characters, such as numbers or upper case letters.
PayPal
A method of online money transfer and payments.
Peer-to-Peer
A distributed that shares tasks or work between devices of the same level.
Phishing
A fraudulent attempt to gain personal or sensitive information, by sending an email or creating a
website that pretends to be from a real company or person, but is not.
Play Store
Goggle’s app store, where users can download or purchase programs to run on their Android devices.
Podcast
A digital audio file made available on the Internet for downloading to a computer or mobile device,
typically available as a series, new installments of which can be received by subscribers automatically.
Post
A message, comment, image, or other item that is placed on the internet, generally on a website.
Predictive Text
An input technology that guesses what you want to type both from what you are currently typing and,
if you have allowed the software to learn, from what you have typed in the past. Predictive text makes
typing faster and easier if you have good software on the back end.
Privacy
The information that is shared between your device and the external resources to which it is
connected, as well as how that information is used, and with whom that information is shared.
Program
A program is a piece of software that lets your device do something like send a text message or video
chat. A program is the same thing as an application.
Public Network
An electronic connection where the traffic between devices is visible to anyone.
Reply All
A response to an electronic message that is returned to ALL recipients of the original message.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 45
Reply
A response to an electronic message.
Ripping
Extracting digital content from a container, such as a CD or DVD. Ripping a CD means that the music
is copied without loss from the CD to your computer.
ROT-13
One of the most basic forms of encryption; a substitution encryption where characters are rotated 13
places.
Router
A networking device that forwards data between networks.
RTFM
Read The Fantastic Manual.
Scraping
Web scraping, web harvesting, web data extraction is extracting data from websites—gathering up
information available on a public website.
SD Card
Secure Digital card. Removable memory that is used in devices like cameras, because it can be easily
switched out when full. Allows for easy transfer of files from device to computer without a cable.
Search Engine
A software system designed to find information on the web. The results from a search engine can be
webpages, files, or images. Generally, behind the scenes a program runs an algorithm that crawls
through the web cataloging everything it sees. This catalog is then organized by a different program
where pages are associated with various terms.
Security
Protecting electronic systems from theft or damage. This can be protection from physical theft, but
often refers to electronic damage, where systems can be disrupted or data stolen.
Server
A device (or program) that allows you to access something not on the device you are physically
touching. A mail server stores your email and drops it to your device upon request. A web server
allows you to connect to the internet.
Settings
An app that allows you to customize your computer, device, or program.
Siri
Apple’s personal assistant.
Smart Device
An electronic device that connects to other devices or the internet through a wireless protocol such as
Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
SMS
Short Messaging Service. A brief message that is sent from one phone number to another phone
number. SMS does not use cellular data.
Snooping
Unauthorized listening in to data transmission.
Snopes
One of the first internet fact-checking resources, Snopes started as a site to debunk urban legends, but
expanded into general fact-checking. (https://www.snopes.com/)
Social Media
Interactive computer technologies and websites that allow for the sharing of information. Facebook is
the most famous social media site, and allows friends to connect automatically, but LinkedIn is
another type of social networking site, that focuses on career and job networking.
Software
The programs that run on your computer or phone. Can also be called an application.

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 46
Spam
Unsolicited electronic messages (especially advertising).
Spoofing
When a person or program pretends to be someone else, by falsifying data, to gain access to your
account or data.
Spyware
A piece of malicious software that secretly installs itself to gather information about the user or
device.
Status Bar
A graphical element, usually at the top or bottom of a device’s screen, that displays information about
the state of the device. Some settings commonly found on the status bar are sound/volume, time, and
battery life.
Sync
See synchronize.
Synchronize
When a file is synced, changes to that file are saved are pushed from one device to all other devices
with access to that file, via a remote server.
Tag / Tagging
A keyword or term added to the metadata of a piece of information. In social media, when someone is
tagged, they are alerted to a post made by another user.
TB
Terabyte. A measure of computer storage equal to 1000 gigabytes or trillion bytes. The prefix tera
means 10
12
.
Terms of Service
The rules you agree to abide by when you sign up use an online service.
Text Message
A brief message that is sent from one phone number to another phone number via a protocol called
SMS. Text messages are generally limited to 160 characters, and messages with more characters than
that will be broken down into multiple messages when sent. Text messages are asynchronous:
a message sent to someone whose phone is off is delivered when their phone is turned back on. Text
messages generally do not require cellular data but do require a cellular connection.
Thumb Drive
USB Flash Drive
Timeline
A display of items in chronological order. Twitter has a timeline; Facebook has a news feed.
TL;DR
Too Long, Didn’t Read
TOS
Terms of Service
Trojans
A type of malicious computer virus that presents itself as a useful item, such as a document.
Two-Factor Authentication
This is a way to make both your device and your account more secure. When you log into your Apple
ID on a new iPad (or iPhone) for the first time OR you log into iCloud from a computer you have
never used before, Apple wants you to verify that YOU are the person attempting to access your
account.
TXT
Text message.
Unfollow
To stop seeing a user’s posts in your timeline or news feed. On Facebook, you can unfollow someone
by still remain friends with them.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 47
Uninstall
The removal or a software program or application from the operating system of a device. Although
uninstall removes the visible aspects of a program, there are often bits and pieces of the program left
behind.
Unique Identifier
A piece of data that is unique to a record. Telephone numbers and email addresses are often used as
unique identifiers, because no two individuals have the same ones. Unique identifiers allow data
records to be linked across databases.
Upload
To move files from your computer to a cloud service or network.
URL
Uniform Resource Locator is the address of a space on the web. Every website has a unique address,
and that address can often tell you something about the web page you are visiting.
USB
Short for Universal Serial Bus, this is the industry standard for cables that connect devices and their
peripherals through a wire. This connection can be used for both communication and power. There
are several types of USB connections: USB, USB-mini, USB-micro, and the newest standard, USB-C.
USB Flash Drive
A small USB data storage device that is removable, rewritable, and can be easily carried in a pocket.
User Data
Any type of data generated by people interacting with software programs. User data includes:
Explicit Data, which is given by a user directly such as name, address, email, and phone number;
Implicit Data, which is not provided by the user directly but gleaned through analysis of user
interactions, such as pages visited, session duration, or type of device; and finally External Data which
has been gathered from third parties with whom an organization has a relationship.
Username
Also called Account name, login ID, user ID. The credentials you use to access an electronic resources,
such as your computer or a website. Every account on a website or device must be unique to that
service, so as to keep account information separate.
Virtual Personal Assistant
A software program that preforms tasks or services based upon verbal commands. Some of the most
well-known services are Siri and Alexa.
Viruses
A piece of malicious software that inserts itself into another software program that it uses to replicate
itself. Ransomware is a software virus.
Web
Also called the World Wide Web, this is an information space on the Internet that is accessible from
devices such as computers, cell phones, and tablets, using a URL as the address.
Web Browser
A software program that allows you to access sites on the Internet, or web.
Web Cookie
See Cookie.
Website
a location connected to the Internet that maintains one or more pages on the World Wide Web
Wi-Fi
Short for wireless (the “fi” is an arbitrary syllable added on)
Widget
A graphical element that displays information or provides quick access to certain parts of an app.
Mobile devices frequently have a weather widget that is linked to your weather app, and which tells
you the current temperature and forecast.
Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 48
Wireless Access Point
A device that allows your device to access the internet. If a wireless access point (or router) does not
have a password, it is unsecure, and you should assume that anyone can see what you are doing on
your device.
Wireless Router
A piece of hardware that allows devices to connect to the internet without being plugged into the wall.
Your wireless at home should be password protected, so that strangers cannot access all devices in
your home using that wireless network.
Wireless
A technology that allows computers to connect to a network and/or the internet without using a
physical connection. Wireless is available in an area when a wireless access point (also called a
hotspot) has been created and made accessible to devices. Public wireless is less secure and caution
should be used (ie, don’t make purchases or send private emails over a wireless network). Private
wireless networks (such as in your home) should be secured with a password.
World Wide Web
An information system on the Internet which allows documents to be connected to other documents
by hypertext links, enabling the user to search for information by moving from one document to
another.
Index
To Access Android Settings .............................. 4
Changing Font Size ........................................... 5
Toggling Flash Alerts ........................................ 6
Finding Your Device Information .................... 6
Changing Your Screen Timeout ....................... 7
Removing a Home Screen ................................ 8
Adding a Home Screen ..................................... 8
Removing Apps and Folders from the Home
Screen ............................................................... 8
Adding a Widget ............................................... 9
Opening your App Drawer .............................. 11
Selecting what Accounts are Synced ............... 13
Setting Your Emergency Contacts ................... 16
To Turn Wireless Off and On ......................... 18
To Select a Wireless Network ......................... 18
Sending Text Messages ................................... 19
Closing Apps ................................................... 20
Force Stopping Apps ....................................... 21
Uninstalling Apps ............................................ 21
Finding and Installing New Apps ................... 21
Creating a Folder ............................................ 23
Adding Apps to a Folder ................................. 24
Using Your Cell Phone Camera ...................... 25
Taking a Selfie ................................................. 25
Camera Settings .............................................. 25
Photo Settings ................................................. 26
Selecting Photos ............................................. 26
Sharing Photos ................................................ 27
Checking for an SD Card ................................ 27
Transferring Apps to the SD Card .................. 28
Changing the Save Location for New Pictures29
Setting up Google Drive on Your Computer .. 30
Accessing Backup and Sync ............................ 33
Adding a Bluetooth Device ............................. 34
Setting Up Smart Lock ................................... 35
Texting Apps that Work over WiFi ................ 36
Cloud Services ................................................. 36
Android Voice Commands ............................. 36
Please Support OLLI@WVU!
Osher Lifelong Learning Institute
Mountaineer Mall Unit C-17
PO Box 9123
Morgantown, WV 26506-9123

Created by Michelle for OLLI@WVU 49
Phone Numbers:
Office: (304) 293-1793
Email Address: ol[email protected]u.edu
http://www.olliatwvu.org
